FortiGate firewall always surprise me with his rich embedded features, prices and performance. FortiOS is a security-hardened, purpose-built operating system that is the software foundation of FortiGate products. With this one unified intuitive OS, we can control all the security and networking capabilities across all of your Fortigate products.
FortiGate firewall always surprise me with his rich embedded features, prices and performance. FortiOS is a security-hardened, purpose-built operating system that is the software foundation of FortiGate products. With this one unified intuitive OS, we can control all the security and networking capabilities across all of your Fortigate products.
I put some of useful commands or configurations in following two posts:
- FortiOS Configuration for FortiGate Firewalls (Commands) 1
- FortiOS Configuration for FortiGate Firewalls (Commands) 2
1. Debugging and Diagnostic your system
diag debug enable
diag debug console timestamp enable
diag sniffer packet wan 'host 8.8.8.8' 1
diag debug disable
diag debug reset
diag debug cli cmd will show you the “cli commands” for actions that you take from the gui.
diag debug enable diag debug cli 8
diag sys flash list command will show you the partition image files in your flash.
FWF60D # diag sys flash list Partition Image TotalSize(KB) Used(KB) Use% Active 1 FWF60D-5.06-FW-build1486-170816 253871 48877 19% No 2 FWF60D-6.00-FW-build0163-180725 253871 53598 21% Yes 3 ETDB-1.00000 3368360 81632 2% No Image build at Jul 25 2018 19:06:34 for b0163
diag sys tcpsock command will show you the active opening ports in your system.
FWF60D # diag sys tcpsock 0.0.0.0:10400->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x8 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:5060->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x102 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:135->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x2 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:1004->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x8 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:1005->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x2 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:7822->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x1 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:910->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x1 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:80->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x1 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:80->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x2 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:10000->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x8 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:2000->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x102 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 0.0.0.0:1010->0.0.0.0:0->state=listen err=0 sockflag=0x2 rma=0 wma=0 fma=0 tma=0 ......
1.1 Debug VPN
Enable Debugging
FWF60D #diag debug enable FWF60D #diag debug console timestamp enable
FWF60D #diag vpn ike log-filter dst-addr4
FWF60D #diag debug application ike -1
FWF60D # tree diag vpn ike gateway
|
-- gateway -- list -- name -- <name> (0)
|
|- clear -- name -- <name> (0)
|
+- flush -- name -- <name> (0)
|
Disable Debugging
FWF60D #diag debug disable FWF60D #diag debug console timestamp disable FWF60D #diag debug application ike 0
Show active tunnel and gateway list
FWF60D #diag vpn tunnel list FWF60D #diag vpn gw list
2. Get system configuraiton
get system arp // ARP Table
get system dns // DNS Configuration
get system dhcp server // DHCP server configuration
FGT30D # get system setting
opmode : nat
firewall-session-dirty: check-all
bfd : disable
utf8-spam-tagging : enable
wccp-cache-engine : disable
vpn-stats-log :
vpn-stats-period : 0
v4-ecmp-mode : source-ip-based
gui-default-policy-columns:
asymroute : disable
ses-denied-traffic : disable
strict-src-check : disable
asymroute6 : disable
per-ip-bandwidth : disable
sip-helper : enable
sip-nat-trace : enable
status : enable
sip-tcp-port : 5060
sip-udp-port : 5060
sccp-port : 2000
multicast-forward : enable
multicast-ttl-notchange: disable
allow-subnet-overlap: disable
deny-tcp-with-icmp : disable
ecmp-max-paths : 10
discovered-device-timeout: 28
email-portal-check-dns: enable
show system interface wan1 | grep -A2 ip // Show WAN and interface information.
get system info admin status // Show logged in users
get system status // Show system hardware/software update versions
get hardware status // Detailed hardware model information
get system performance status // Check System Uptime
FGT30D3X12001671 $ get system performance status CPU states: 0% user 0% system 0% nice 100% idle CPU0 states: 0% user 0% system 0% nice 100% idle Memory states: 21% used Average network usage: 3 kbps in 1 minute, 0 kbps in 10 minutes, 0 kbps in 30 minutes Average sessions: 14 sessions in 1 minute, 11 sessions in 10 minutes, 11 sessions in 30 minutes Average session setup rate: 0 sessions per second in last 1 minute, 0 sessions per second in last 10 minutes, 0 sessions per second in last 30 minutes Virus caught: 0 total in 1 minute IPS attacks blocked: 0 total in 1 minute Uptime: 106 days, 0 hours, 8 minutes
get system performance top
show system interface
diagnose hardware deviceinfo nic // Interface Statistics/Settings
diagnose hardware sysinfo memory
diag debug crashlog read
diag hardware sysinfo shm // Device should be in 0, if (>0) then conservemode
get system global | grep -i timer // Show tcp and udp timers for halfopen and idle
get system session-ttl // System default tcp-idle session timeout
get hardware nic
get system interface physical
diagnose ip address list
diagnose ip arp list
diagnose sys session list
diagnose sys session clear
diagnose sys kill 9 <id>
3. Change Bult-in Internal Switch to Interface mode
In Switch mode, all the internal interfaces are part of the same subnet and treated as a single interface, called either lan or internal by default, depending on the FortiGate model. Switch mode is used when the network layout is basic, with most users being on the same subnet.
In Interface mode, the physical interfaces of the FortiGate unit are handled individually, with each interface having its own IP address. Interfaces can also be combined by configuring them as part of either hardware or software switches, which allow multiple interfaces to be treated as a single interface.
a. Command to change the FortiGate to switch mode:
config system global
set internal-switch-mode switch
end
b. Command to change the FortiGate to interface mode:
config system global
set internal-switch-mode interface
end
After changed internal switch from switch mode to interface mode, you will be able to move some interface out of Internal switch and they will become routing interfaces for you to do configuration.
Here is a user case. HA implementation will need two routing ports. If you change your switch to interface mode, you will be able to use two LAN ports for HA purpose.
Note: How to Change Switch Mode to Interface Mode in Fortigate FortiOS 5
4. Daily System Scheduled Reboot
config system global set daily-restart enable set restart-time 05:06 end
Note: For weekly reboot, you will need expect command with a script.
5. Some HA Commands
Manual Failover HA
diagnose sys ha reset-uptime
Mange Cluster Member from Console
Test-1 # get system ha status
Model: FortiGate-60D
Mode: a-p
Group: 0
Debug: 0
ses_pickup: disable
Master:250 Test-1 FGT60D4614041798 1
Slave : 50 Test-2 FGT60D4Q15005710 0
number of vcluster: 1
vcluster 1: work 169.254.0.2
Master:0 FGT60D4614041798
Slave :1 FGT60D4Q15005710
Test-1 # execute ha manage 0
Test-2 $
Test-2 $ execute reboot
This operation will reboot the system !
Do you want to continue? (y/n)y
6. One to One Inbound NAT Configuration
WAN IP Address : 192.168.20.200
LAN IP Address: 192.168.2.200
Rule: Allow Any External IP Address to access LAN Server 1921.68.2.200 on SMB (TCP 445 – File Sharing Port), but not expose LAN IP Address.
6.1 Create VIP address
6.2 Create firewall Rule
Note: No NAT configuration. NAT will be taken care by VIP configuration in step 6.1
Destination will be External IP Address.
6. Tree command
Tree command can be used to display the command tree for a configuration section.
FWF60D # tree execute ping-option |
-- ping-options -- data-size -- <integer> (0)
|
|- df-bit -- <string> (0)
|
|- pattern -- <string> (0)
|
|- repeat-count -- <string> (0)
|
|- source -- <string> (0)
|
|- interface -- <string> (0)
|
|- timeout -- <integer> (0)
|
|- adaptive-ping -- <string> (0)
|
|- interval -- <integer> (0)
|
|- tos -- <string> (0)
|
|- ttl -- <integer> (0)
|
|- validate-reply -- <string> (0)
|
|- view-settings
|
+- reset
FWF60D # tree system ddns
-- [ddns] --*ddnsid (0,4294967295)
|- ddns-server
|- ddns-server-ip
|- ddns-zone (65)
|- ddns-ttl (60,86400)
|- ddns-auth
|- ddns-keyname (65)
|- ddns-key
|- ddns-domain (65)
|- ddns-username (65)
|- ddns-sn (65)
|- ddns-password
|- use-public-ip
|- update-interval (60,2592000)
|- clear-text
|- ssl-certificate (36)
|- bound-ip
+- [monitor-interface] --*interface-name (65)
FWF60D #
|
7. Disable Local Logs
If you donot want to log your local logs, here is a way to disable it. But you may lose some view of local broadcasting noise.
FWF60D # config log memory filter
FWF60D (filter) # set local-traffic disable
FWF60D (filter) # end
FWF60D #
8. Configuration Example
Fortigate Device Information:
LAN : 192.168.200.1/24
WAN : 85.86.87.2/29
Default Gateway to ISP: 85.86.87.1
|
config system global
# Set the http admin port to 80/tcp set admin-port 80 # Set the https admin port to 443/tcp set admin-sport 443 # Set the ssh admin port to 22/tcp set admin-ssh-port 22 # Set the telnet admin port to 23/tcp set admin-telnet-port 23 # Set the hostname set hostname “FW-Office-1” # Set the ntp server to “0.ca.pool.ntp.org” and enable it set ntpserver “0.ca.pool.ntp.org” set ntpsync enable # Set to 43200 seconds the tcp-halfclose timer set tcp-halfclose-timer 43200 end # Set the telnet 23/tcp port timeout to 43200 seconds. config system session-ttl set default 43200 config port edit 23 set timeout 43200 next end # Set the IP address and administrative access options (ping https http) for lan interface. config system interface edit “lan” set ip 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 set allowaccess ping https http set type physical next # Set the IP address and administrative access options (ping https) for wan interface. # Set “gateway Detect” option enable and set the “Ping Server” destination. # Set the interface speed to 10 Mb/s Half Duplex, this is useful for some connections like radio bridge. edit “wan1″ set ip 85.86.87.2 255.255.255.248 set allowaccess ping https set gwdetect enable set detectserver “85.86.87.23″ set type physical set speed 10half next end # Set DNS Servers and DNS options config system dns set primary 192.168.200.3 set secondary 8.8.8.8 set domain ” set autosvr disable set dns-cache-limit 5000 set cache-notfound-responses disable end # Set a firewall policy to enable traffic from lan TO WAN using NAT # Set a protection profile (a default one) called “scan” config firewall policy edit 1 set srcintf “lan” set dstintf “wan″ set srcaddr “all” set dstaddr “all” set action accept set schedule “always” set service “ANY” set profile-status enable set profile “scan” set nat enable next end # Set a default gateway on the WAN interface config router static edit 1 set device “wan″ set gateway 85.86.87.1 end |
9. Proper shut down of FortiGate unit
To limit unnecessary logdisk or flash failure, Fortinet recommends that you always use the shutdown (or restart) commands when shutting down or rebooting any FortiGate unit.
Never shut off a FortiGate unit by removing power from the unit.
To power off a FortiGate unit correctly
- Issue the Shutdown Command.
From the web-based manager, go to System> Maintenance> ShutDown, Select Shut Down and click on Apply.
From the CLI, enter
execute shutdown - Disconnect the power supply.
10. BGP
get router info bgp summary
11. Restrick Access to Web and SSL VPN
1. For FortiGate Web Portal
sh full firewall local-in-policy
config firewall local-in-policy
edit 1
set uuid d7f13336-22a0-51ef-ee79-444132007804
set intf "port1"
set srcaddr "Allowed_Countries"
set srcaddr-negate enable
set dstaddr "wan-10.254.3.5/32"
set internet-service-src disable
set dstaddr-negate disable
set action deny
set service "ALL"
set service-negate disable
set schedule "always"
set status enable
set comments ''
next
end
Notes:https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.4.4/administration-guide/363127/local-in-policy
If a local-in-policy is not functioning correctly and traffic that should be blocked is being allowed through, the issue may be that the implicit deny local-in-policy has not been created. Unlike IPv4 policies, there is no default implicit deny policy. The implicit deny policy should be placed at the bottom of the list of local-in-policies. Local-in-policies are created for each interface, but if you want to create a general implicit deny rule for all interfaces for a specific service, source, address, or destination address, use the any interface.
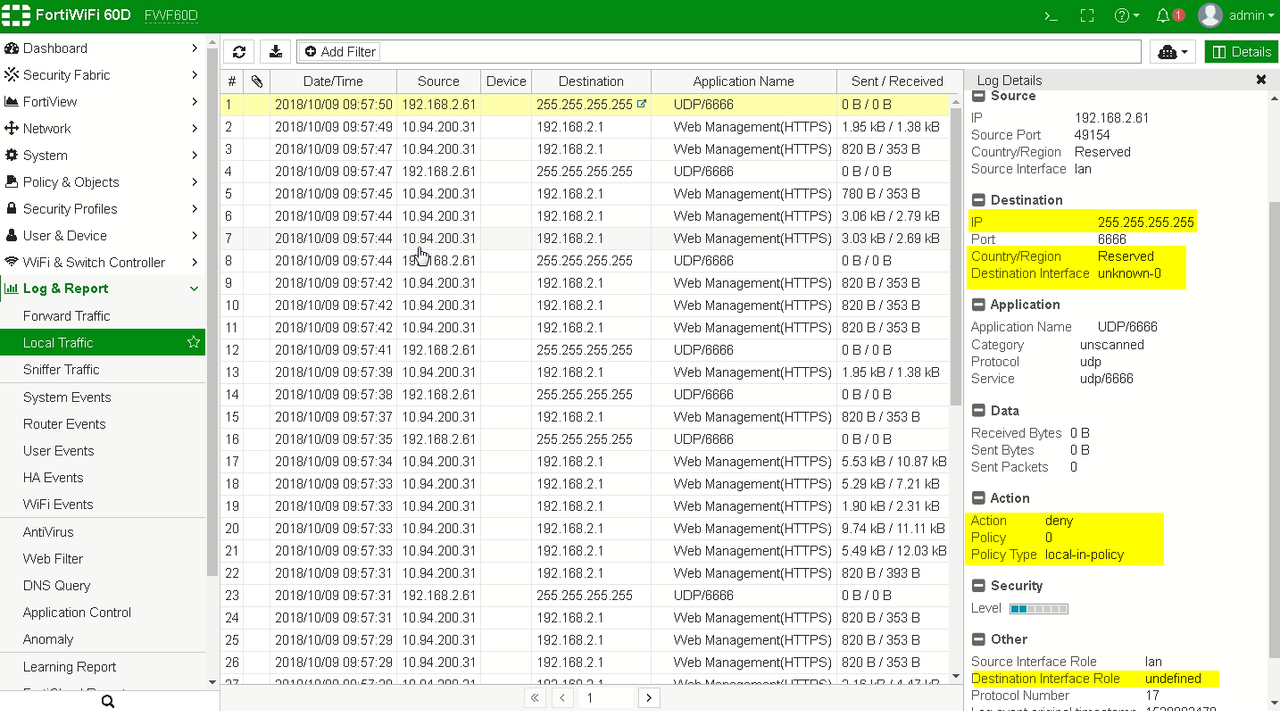
View default Local In Policy from Web GUI:
2. For SSL VPN
- Using Geograph Limitation
- Extend Lock time from 60 seconds to 600 seconds when user failed log in using the combination of username and password.
This indicates if user enters incorrect username/password combinations continuously twice, the firewall will block attempts and prompt with message as ‘Too many bad attempts. Please try again in few minutes’.
FGT # config vpn ssl settings
FGT (settings) # show
config vpn ssl settings
set banned-cipher SHA1 SHA256 SHA384
set servercert “Fortinet_Factory”
set tunnel-ip-pools “SSLVPN_TUNNEL_ADDR1”
set port 4443
set source-interface “port1”
set source-address “all”
set source-address6 “all”
set default-portal “tunnel-access”
config authentication-rule
edit 2
set groups “Remote Users”
set portal “tunnel-access”
next
end
end
FGT (settings) # sh full
config vpn ssl settings
set status enable
set reqclientcert disable
set ssl-max-proto-ver tls1-3
set ssl-min-proto-ver tls1-2
set banned-cipher SHA1 SHA256 SHA384
set ciphersuite TLS-AES-128-GCM-SHA256 TLS-AES-256-GCM-SHA384 TLS-CHACHA20-POLY1305-SHA256
set ssl-insert-empty-fragment enable
set https-redirect disable
set x-content-type-options enable
set ssl-client-renegotiation disable
set force-two-factor-auth disable
set servercert “Fortinet_Factory”
set algorithm high
set idle-timeout 300
set auth-timeout 28800
set login-attempt-limit 2
set login-block-time 600
set login-timeout 30
set tunnel-ip-pools “SSLVPN_TUNNEL_ADDR1”
set dns-suffix ”
Changed default login-block-time from 60 to 600 (seconds)