What is Cybersecurity Architecture: The practice of designing computer systems to ensure the security of underlying data.
More related posts from this blog:
- Cybersecurity Architecture Practice
- Cybersecurity Architecture Knowledge Overview
- Architecture Category
Major Principles
CIA Triad (confidentiality, integrity, and availability)
Confidentiality – Keeping data secure
- Data encryption is one way to ensure confidentiality and that unauthorized users cannot retrieve data for which they do not have access.
- Access control is also an integral part of maintaining confidentiality by managing which users have permissions for accessing data.
- Life science organizations that utilize patient data must maintain confidentiality or violate HIPAA.
- Securing Data in-motion
- Transport Channel Encryption
- Message-level Encryption
- Securing Data At Rest
- Disk Level Encryption
- File-Level Encryption
Integrity – Keeping data clean
- Event log management within a Security Incident and Event Management system is crucial for practicing data integrity.
- Implementing version control and audit trails into your IT program will allow your organization to guarantee that its data is accurate and authentic.
- Integrity is an essential component for organizations with compliance requirements. For example, a condition of the SEC compliance requirements for financial services organizations requires providing accurate and complete information to federal regulators.
- Message Authentication Code (MAC)
- Hash-Based Message Authentication Code (HMAC)
- Digital Signatures
- Message Digest
Availability – Keeping data accessible
- Employing a backup system and a disaster recovery plan is essential for maintaining data availability should a disaster, cyber-attack, or another threat disrupt operations.
- Utilizing cloud solutions for data storage is one way in which an organization can increase the availability of data for its users.
- As the reliance on data analytics expands, the need for data to be available and accessible grows for sectors like financial services and life sciences.
- Denial of Service (DoS)
- Threat Modeling and use of Anomaly Detection tools
- Resource Throttling
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) Based Prevention
- Network Ingress Filtering
Other principles relating to CIA
- MFA
- Password-Less Authentication
- Authentication Models (API and Web Applications) – OAuth, Federated Identity SSO
- Active Directory (AD) Authentication
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
- Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL)
- Access Control Lists (ACL)
- OASIS Extensible Control Access Markup Language (XACML)
- Java Web Token (JWT)
- Non-Repudiation
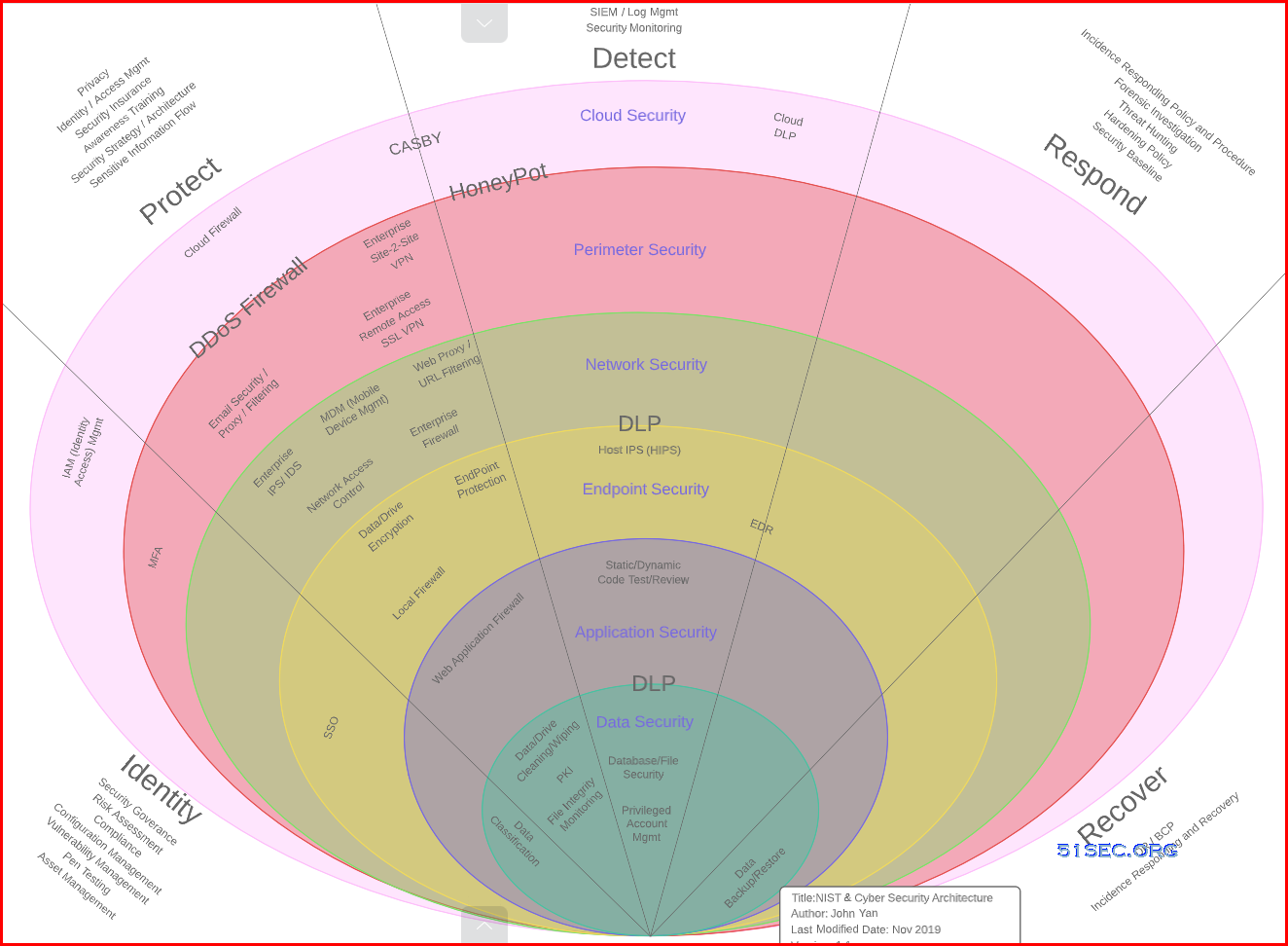
Defense-in-Depth (DiD)
Aka security in depth, refers to a cybersecurity approach that uses multiple layers of security for holistic protection. A layered defense helps security organizations reduce vulnerabilities, contain threats, and mitigate risk.
From: https://lucid.app/lucidchart/271dbc7a-e65f-43e7-a278-ee17240c77a7/edit?page=m-5o7ONTd-nK#
Zero Trust (Assume-Breach)
The key tenets of a modern defense-in-depth strategy include:
- Protect privileged access – use privileged access management solutions to monitor and secure access to privileged accounts (superuser accounts, local and domain administrator accounts, application administrative accounts, etc.) by both human and non-human identities (applications, scripts, bots, etc.).
- Lockdown critical endpoints – use advanced endpoint privilege management solutions to lock down privilege across all endpoints, prevent lateral movement, and defend against ransomware and other forms of malware.
- Enable adaptive multifactor authentication – use contextual information (location, time of day, IP address, device type, etc.) and business rules to determine which authentication factors to apply to a particular user in a particular situation.
- Secure developer tools – use secrets management solutions to secure, manage, rotate and monitor secrets and other credentials used by applications, automation scripts, and other non-human identities.
Zero Trust vs Defense in Depth
PPT – Three Pillars Model
Three Major Elements (PPT) – Three Pillars Model:
- People : Trained with the latest cyber security skills and qualifications to implement the controls, technologies, and best practices for your organisation.
- Cyber savvy board of directors.
- Cybersecurity officer with team having sound technical knowledge of risk management, compliance, incident response, IAM specialist, security monitoring and analyst, vulnerability and patch management, Security Architecture, audit.
- Data protection /security officer.
- People skill management program & Process to identify cybersecurity knowledge
- Cybersecurity operation embedded program for employees.
- Cybersecurity awareness & training for employees.
- Strategy on whether outsourcing of security professional or developing in house expertise, Also dependency on vendor till what extend, Need to define ?
- IT /Security People should be business enabler, It has been seen people unable to perform business function due to tight security control ?
- Process : Bring in a coherent structure, and way of working to mitigate risks or deal with threats in real-time. Continually update documents because hackers are constantly evolving their attack techniques.
- Cybersecurity strategy planning.
- Information security management program.
- Cybersecurity posture assessment & gap analysis.
- Cybersecurity risk assessments Strategy
- Cybersecurity Policy and Procedure Framework.
- Design & Implementation of business continuity management system.
- Security Architect Design & Secure Network Architecture Review.
- Cyberthreat intelligence & Threat modelling.
- IT security governance model.
- Cyber Crisis & Release management Process.
- Cybersecurity Assessment program & Audits.
- Cybersecurity Assurance & compliance management Program.
- Vulnerability Threat Risk Framework.
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing.
- Identity of People & Assets, Secure Access & Authorization policies.
- Privacy & data protection policies & procedure.
- Data Management & Data recovery processes.
- Policy for Utilisation & Maintaining Security Appliances & Security software.
- Incident Response & Management process.
- Continuous monitoring and assessment process.
- Active vulnerability scanning and threat detection from a 24-hour operation
- Baseline your assets with CIS benchmark.
- Information security metrics framework.
- Third party risk management & Mitigation program.
- Cybersecurity awareness training program.
- Cyber resilience Strategy.
- Cyber Insurance policy program
- Implementing continuous process improvements.
- T(echnology) or T(ools) : Technology without a doubt raises the levels of defence. However, if implemented without proper planning, or a limited understanding of the environment it is intended to defend, it will become a root cause of many more problems.
- Perimeter Security : Perimeter firewall, IDS/IPS, Application Gateway firewall, physical security, Deception, Mail security, DNS Security, Secure DMZs.
- Network Security : Network firewall, UTM, Secure remote access,NAC, Inline Patching, Wireless access control , VOIP security.
- End Point Security : EDR, AMP/Anti-virus/Anti-Malware , Browser Isolation, End Point Encryption, Endpoint DLP, Sandboxing/APT, Mobile device security.
- Application Security : Devsecops : SAST,DAST,RASP, IAST, SCA, WAF,API Security, D-DOS Services, CDN security, Bot Management, Database security.Application Encryption, Application shielding. Application security testing, Secure coding practices.
- Data Security : Data discovery, Data classification, Data Encryption, Data Masking/Tokenization, IAM,PAM, Key Management, DLP, FIM, EDRM,FIM,SFTP, (Data Backup & recovery).
- Security operation : SIEM,XDR, SOAR, Log management, UBA.
- Cloud Security : CSPM,CWPP,CASB,CIEM, Docker Container Security.
PPT Design Example:
360° Cybersecurity approach (or Framework)
Step 1 is to identify and assess your current level of threat, risks and protection.
Identify –> Threat—-> Risk —-> Strategy —-> Security review.
Step 2 is to take corrective action where gaps are identified.
Protect –> People —->Process —-> Technology.
Step 3 is to monitor the system, respond to threats and incidents and allow you to report to your board and regulators”
Monitor –> Real Time —->Scheduled—->Unscheduled —-> Security Review.
(These steps explained in below infographics)

Cybersecurity (People + Process + Technology) = Successful Organization Transformation.

Common Cybersecurity Related Frameworks
Key Deliverables:
TOGAF EXAMPLES:
SABSA EXAMPLES:
OSA EXAMPLES:
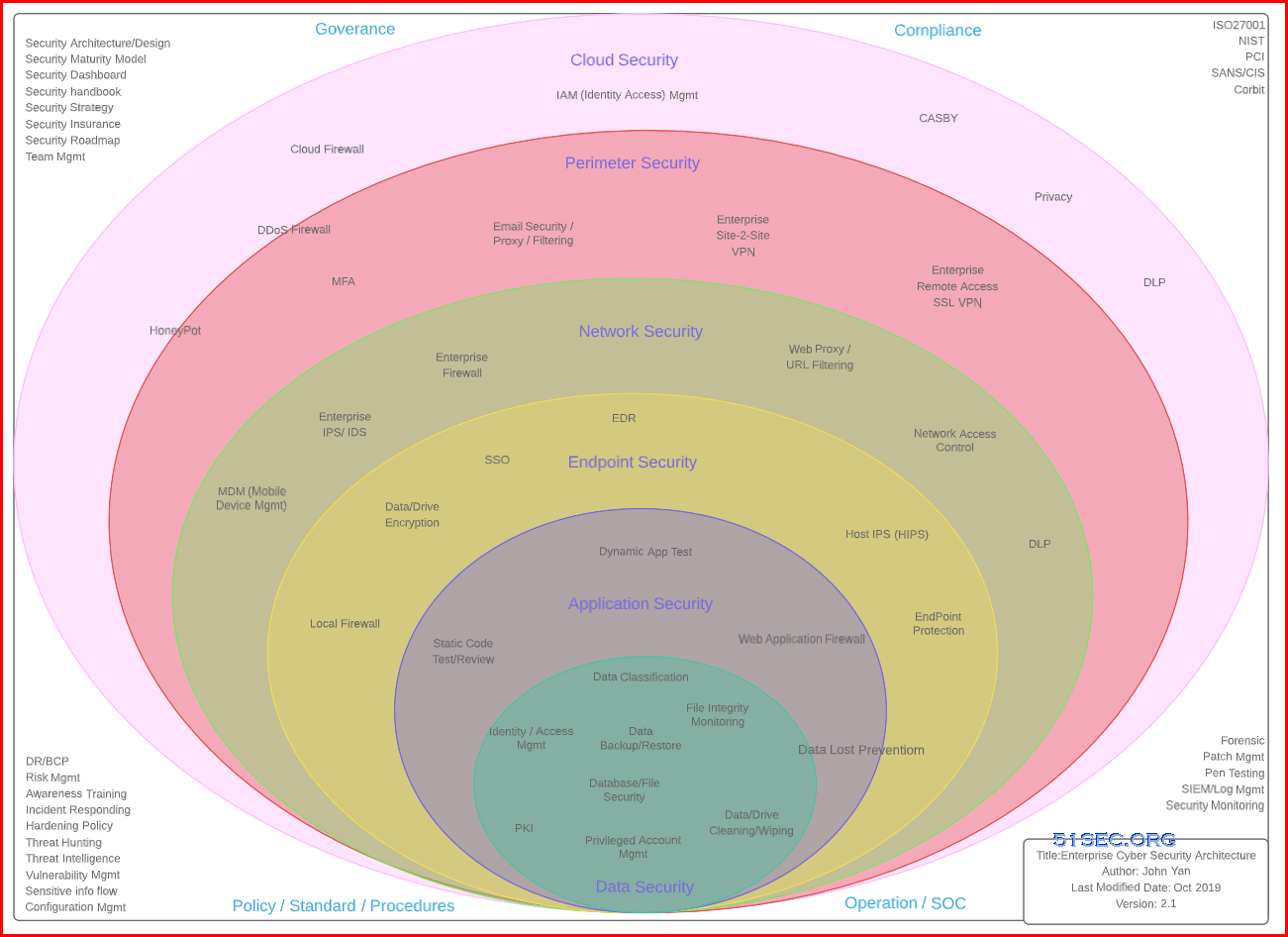
Enterprise Cybersecurity Architecture
From: https://www.jamesjfisher.org/esa/esa.html
- Holistic: Enterprise Cybersecurity Architecture requires a holistic approach when dealing with complex systems across an organization. This means having a proper understanding of requirements, design philosophy, interoperability, component integration, and how the system will operate. Likewise, holistic is not a checklist-based approach, or other necessary components, either technical or process-oriented, may get missed.
- Business-Driven: Enterprise Cybersecurity Architecture must be business-driven, focusing on securely enabling the business’ strategic directions in current and new markets, channels, and products. Therefore, a firm understanding of where the company is today and where the business wants to be in the future is necessary.
- Risk-Driven: An Enterprise Cybersecurity Architecture focuses on a realistic perspective of risks facing an organization and the remedies in terms of security mechanisms to reduce those risks. It is neither cost nor operationally efficient to put security mechanisms in that are not relevant or required based on the risks present or support a risk the organization does not inherently have.
Enterprise Cybersecurity Architecture-Reference Architecture

Enterprise Cybersecurity Architecture-Domain Mapping

Enterprise Cybersecurity Architecture Paradigm-Reference

Cybersecurity and Technology Operations Paradigm-Reference

Secure Design Principles-Reference

Policy and Harmonized Control Framework-Reference

The Cyber Scape from Momentum Cyber

Related Concepts
Four Major or Critical Areas:
- Company policy regularions
- User identity control
- Access controls
- Post implementation review of Cybersecurity framework and technologies
An effective Cybersecurity architecture’s characteristics:
- Constantly find and close blind spots
- Stringent Cybersecurity controls
- End-to-end encryption
- Reducing the infection