This post summarizes how we can use Microsoft 365 to modernize our IT security.
If you are doing it correctly, Microsoft 365 could be your coolest and most practical and cost effective ($20/user/month) IT security and management systems. This is part 1.
- IT Security Modernization with Microsoft 365 – Part 1
- IT Security Modernization with Microsoft 365 – Part 2
Traditional IT security management components
- Domain Controllers
- Domain joined client PC’s
- File server security groups
- On-Premise BDR’s (backup and disaster recovery)
- On-Premise Firewalls
- VPN’s
- Computer setups/imaging
- Computer antivirus
Email security upgrade to Microsoft Defender for Office 365 | Safe Links & Safe Attachments
- Basic spam and malware filter inclided with exchange online
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365
- Safe attachments
- Safe links
- $2/user/month add-on
Now it has been moved to https://security.microsoft.com/securitypoliciesandrules
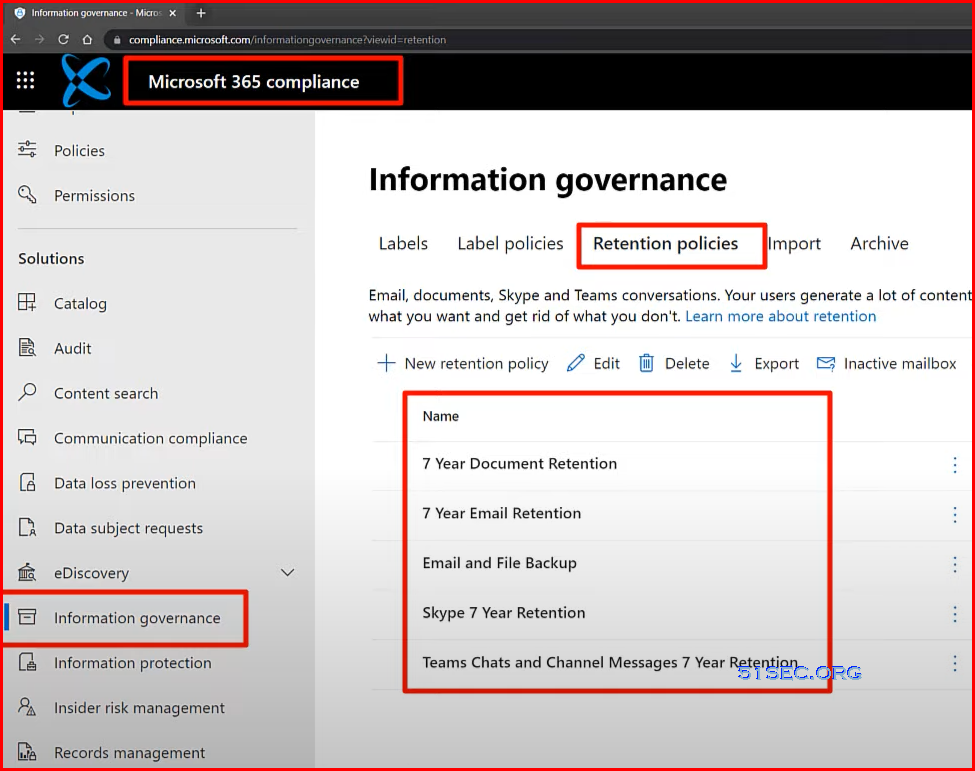
Email “backup” in Microsoft 365 | Retention policies
- Exchange on-premise, local backup
- Using Microsoft Office 365
- Default 15 days exchange online “double-delete” retention policy
- No need to backup email data
- 3 Year then delete exchange online email retention policy
- Customize your retention policy to meet your legal compliance
Microsoft 365 Active Directory (Azure Active Directory)
- Windows Server Active Directory
- Azure Active Directory Premium P1
“Domain join” computers in Microsoft 365 Azure Active Director
- Windows Server Active Directory “Domain join”
- Azure AD Join
- Workplace Join – Personal computers/devices “BYOD”
Azure AD join is your option for the corporate owned, personally enabled (COPE) endpoint device scenario. Because the endpoint is corporate owned, you can enforce policy that wouldn’t work with personally owned devices.
Bring your Own Device (BYOD) in Microsoft 365 | Workplace Join computers in Azure Active Directory
Microsoft 365 Multi factor Authentication
Traditional ways:
- No
- or Admins only
- Azure AD MFA for everyone
App passwords in place of MFA for legacy devices and software service accounts
- App passwords for legacy service accounts
Microsoft 365 Global Password Protection Service
Traditional ways:
Microsoft 365 User Self service password reset
Traditional ways:
- Windows Server AD & Azure AD, manual User Password Resets
- Microsoft 365 User Self-service password resets
- Password write-back to Windows Server AD
Windows OS Logon Modernization | Biometrics
Traditional ways:
- Enter Passwords to Login to Windows
- Your Smartphone has better login experience
- Windows Hello Biometric login
- webcam
- Fingerprint reader
- PIN
- Inexpensive, reliable, secure
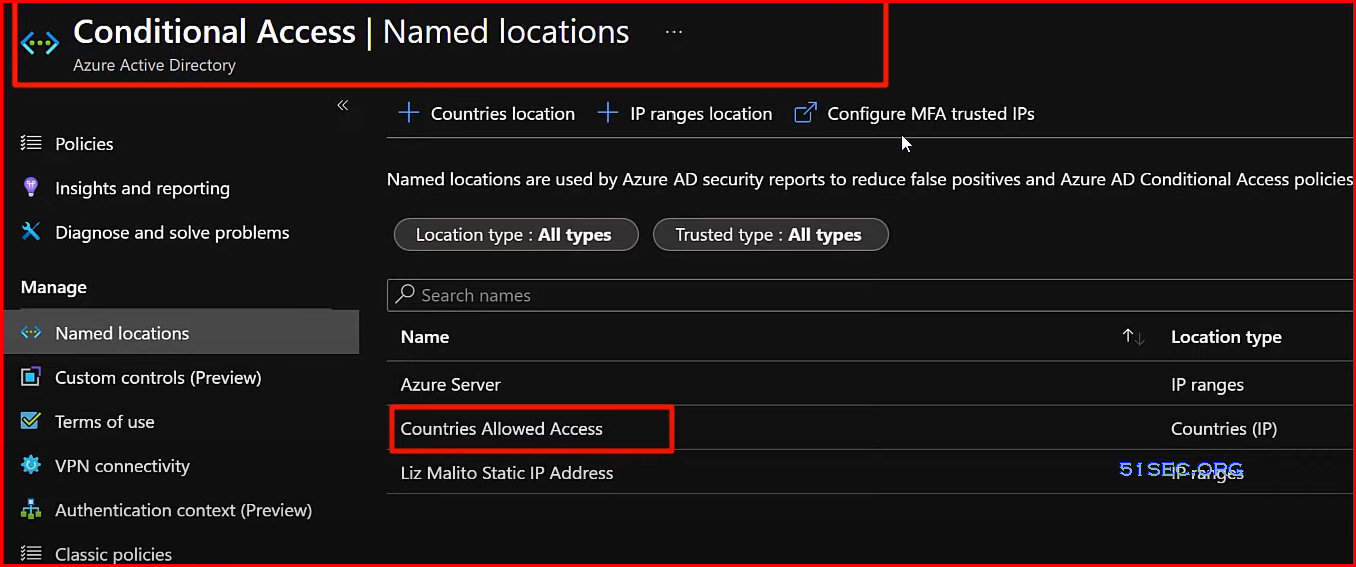
Advanced Microsoft 365 Active Directory & Geographic Sign in Blocks
Traditional ways with your Office 365 default:
- Sign-ins work from anywhere in the world
- Free for all
- Geographic Block
- Sign-ins ONLY work from countries we allow
- Everywhere else is BLOCKED by default with specific TEMPORARY exceptions
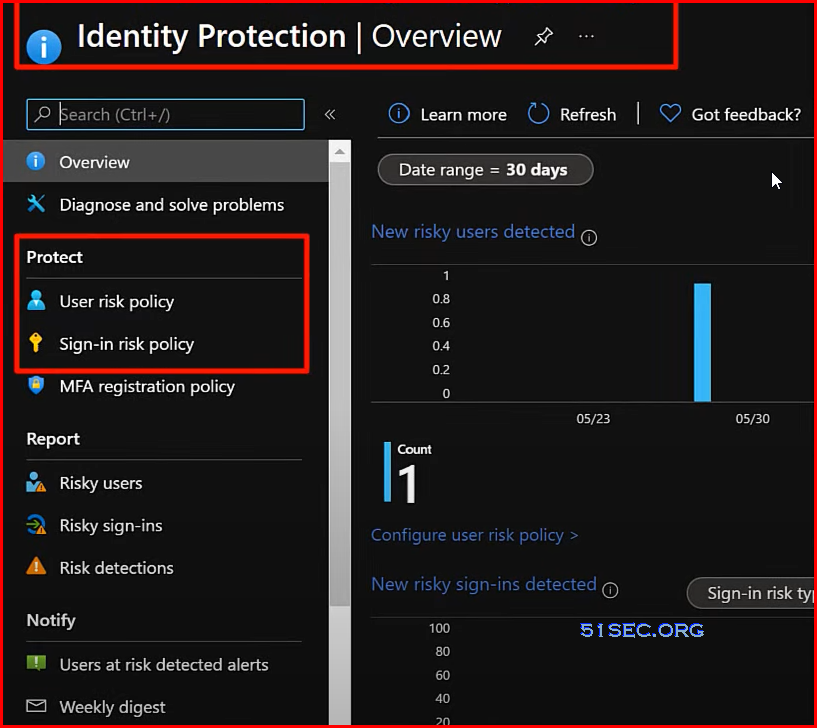
Azure Identity Protection | Machine learning Risky Sign ins & Risky Users
- Upgrade from Azure AD Premium Plan 1 to Plan 2
- Azure Identity Protection
- Risky sign-ins
- Risky users
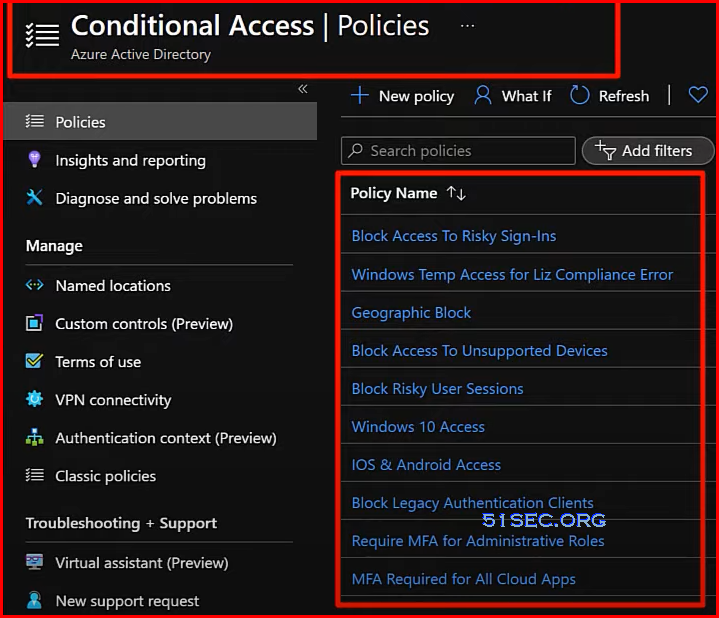
Conditional Access Policies
Traditional ways:
- No minimum security standards to access, work with, store company data
- Conditional Access Policies
- Conditions we require for users to access, work with, and store company data
File shares setup in Microsoft 365 | Teams & SharePoint
Traditional ways:
- Windows Server Department File SHARES
- Teams Channel Files (Highly recommended)
- Or SharePoint Document Libraries
File share security in Microsoft 365 | Teams and SharePoint
Traditional ways:
- Windows Server Department File SECURITY
- Teams – Microsoft 365 Groups
- Or SharePoint Security Groups
User folder setup and security in Microsoft 365
Traditional ways:
- File Server User Folders and Security
- OneDrive
File share security in Microsoft 365 Advanced
- Once users have access to file shares, they can do whatever they wat to do with data
- copy/delete/share/steal
- Nothing is logged or tracked
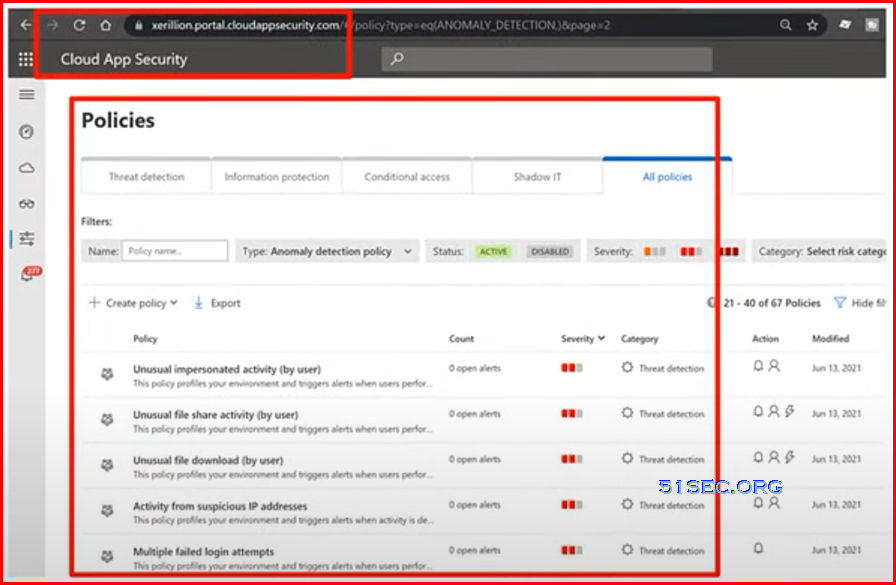
Microsoft Cloud App Security | Insider Threat Protection
- Microsoft cloud app security
- insider threat management
- risk user behavior is continuously tracked
- risky copy/download/share/delete is alerted or blocked
Microsoft has changed the name from Microsoft Cloud App Security to Microsoft Defender for Cloud App
Microsoft 365 Ransomware Crypto locker Antivirus Protection | Microsoft Defender for Office 365
Traditional ways:
- Nothing or Weak (basic email spam filter or anti malware )
- 3rd party Antivirus
- SharePoint/Teams Files/OneDrive
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365
- Safe attachments (i.e., files) in SharePoint, Teams and OneDrive
- Microsoft Cloud App Security
Microsoft 365 File Backups
Traditional ways:
- 3rd party backup software and hardware
- 3rd party online backup services
- Expensive Disaster recovery site
- Microsoft 365
- Document Versioning
- 2 Stage Recycle Bin
- Data Retention Policies
- Preservation Hold Libraries
- Free disaster recovery
- e.g. Legal/HR team files = Forever retention policy
- All other teams files = 7 years then delete
- All document libraries in the same site will have the same policy