The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing unbiased, practical information about application security.
The OWASP Top 10 Web Application Security Risks was created in 2010, 2013, 2017 and 2021 to provide guidance to developers and security professionals on the most critical vulnerabilities that are commonly found in web applications, which are also easy to exploit. These 10 application risks are dangerous because they may allow attackers to plant malware, steal data, or completely take over your computers or web servers.
Meeting OWASP Compliance Standards usually is the First Step Toward Secure Code.
2021
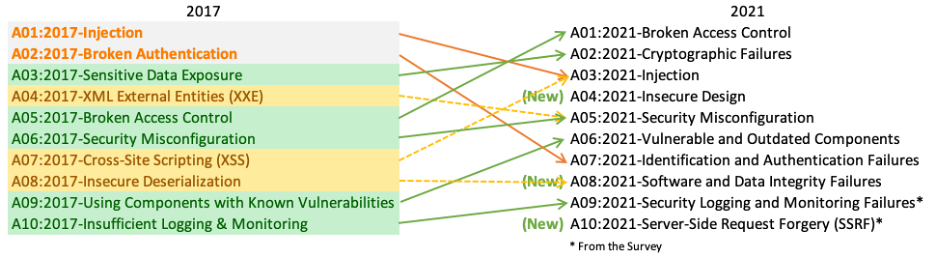
- A01:2021-Broken Access Control
- A02:2021-Cryptographic Failures
- A03:2021-Injection
- A04:2021-Insecure Design
- A05:2021-Security Misconfiguration
- A06:2021-Vulnerable and Outdated Components
- A07:2021-Identification and Authentication Failures
- A08:2021-Software and Data Integrity Failures
- A09:2021-Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
- A10:2021-Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
1. Define Security Requirements2. Leverage Security Frameworks and Libraries3. Secure Database Access4. Encode and Escape Data5. Validate All Inputs6. Implement Digital Identity7. Enforce Access Controls8. Protect Data Everywhere9. Implement Security Logging and Monitoring10. Handle All Errors and Exceptions(From OWASP Proactive Controls for Developers 2018 v3.0)
2017
OWASP Top 10 Application Security Risks – 2017
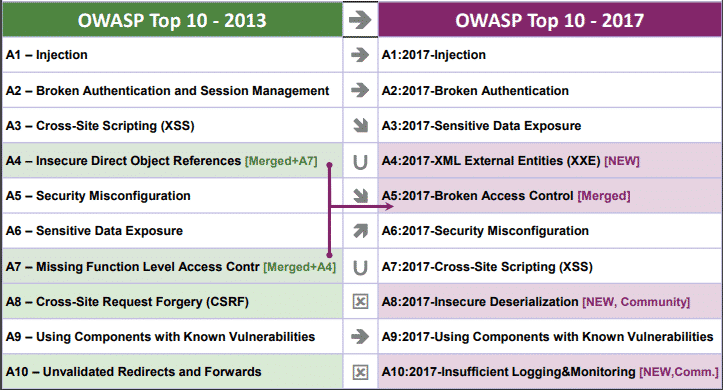
- A1. Injection
- A2. Broken Authentication
- A3. Sensitive Data Exposure
- A4. XML External Entities (NEW)
- A5. Broken Access Control (MERGED)
- A6. Security Misconfiguration
- A7. Cross-Site Scripting
- A8. Insecure Deserialization (NEW)
- A9. Using Components With Known Vulnerabilities
- A10. Insufficient Logging and Monitoring (NEW)
- A1-Injection
- A2-Broken Authentication and Session Management
- A3-Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- A4-Insecure Direct Object References
- A5-Security Misconfiguration
- A6-Sensitive Data Exposure
- A7-Missing Function Level Access Control
- A8-Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- A9-Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- A10-Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards
For 2010, the OWASP Top 10 Most Critical Web Application Security Risks are:
- A1: Injection
- A2: Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- A3: Broken Authentication and Session Management
- A4: Insecure Direct Object References
- A5: Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- A6: Security Misconfiguration
- A7: Insecure Cryptographic Storage
- A8: Failure to Restrict URL Access
- A9: Insufficient Transport Layer Protection
- A10: Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards