High Level Installation Steps:
follow the hardware requirements out of CyberArk Docs system requirements guide
for hardware specs and prerequisite software needed, then do installation as show below.
EPV = Digital Vault + PVWA + CPM
PAS = EPV + PSM
Install Windows 2012 R2 or Windows
2016
Install at least .NET Framework
4.6.2 (if that or a greater version not already included)
Install all the latest Windows OS
patches
The rest is performed during the
install which includes:
Setting up the IIS role via the provided
PVWA prerequisites script.
o Make sure you are using run as administrator to run setup.exe file. Domain admin account will not work
For the
PSMs
Install Windows 2012 R2 or Windows
2016
Install at least .NET Framework
4.6.2 (if that or a greater version not already included)
Install all the latest Windows OS
patches
Add the domain account we are using
to install PSM to the local administrators group of the new PSM VM build
The rest is performed during the
install which includes:
Setting up the Remote Desktop
Session Host role (not from individual checkboxed RD options) and selecting
session-based (which will then ask for connection brokers and RD gateway
servers in later steps).
|
Component
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
PVWA
|
Password Vault Web Access (PVWA) is a fully featured web interface that provides a single console for requesting, accessing and managing privileged accounts throughout the enterprise by both end users and administrators.
|
|
CPM
|
Central Policy Manager is a integral part of the PAS controlling and managing the Master policy. This password management component can change passwords automatically on remote machines and store the new passwords in the EPV, with no human intervention, according to the organizational policy. It also enables organizations to verify passwords on remote machines, and reconcile them when necessary.
|
|
PSM
|
Privileged Session Manager enables organizations to isolate, monitor, record, and control privileged sessions on critical systems including Unix and Windows-based systems, databases and virtual machines. The solution acts as a jump server and single access control point. It prevents malware from jumping to a target system and records keystrokes and commands for continuous monitoring. The resulting detailed session recordings and audit logs are used to simplify compliance audits and accelerate forensics investigations.
|
|
PTA
|
Privileged Threat Analytics is an expert system for privileged account security intelligence, providing targeted, immediately actionable threat alerts by identifying previously undetectable malicious privileged user and account activity. The solution applies patent pending analytic technology to a rich set of privileged user and account behavior collected from multiple sources across the network. CyberArk Privileged Threat Analytics then produces highly accurate and immediately actionable intelligence, allowing incident response teams to respond directly to the attack.
|
PVWA Installation:
1. Pre-installation. Run PVWA_Prerequisites script. After done, review logs and verify IIS service.
2. Installation. Run setup.exe as administrator. After done, review logs and verify web login using Chrome browser.
3. Post-installation. Run hardening script and do manual hardening based on CyberArk Secure PVWA guide.
Install the PVWA (Password Vault Web Access ) server prerequisites
The PVWA_Prerequisites script automates PVWA server prerequisites by doing the following:
- Installs Web Server Roles
- Disables IPv6
- Configures the self certificate
-
In the installation package, open the InstallationAutomation folder, and locate the PVWA_Prerequisites.ps1 file.
-
Open the PowerShell window, then run this file.
-
Reboot the server.
Web Server roles
Log onto Windows as the Administrator user
Before beginning installation, log onto Windows as the Administrator user.
Installation
The Password Vault Web Access must be installed on a different machine to the Enterprise Password Vault server.
- On the PVWA machine, create a new folder and copy the Password Vault Web Access folder from the installation package to it.
-
Start the installation procedure: Double-click Setup.exe
- Click next to go to next step until to this window to select the type of Password Vault Web Access to install.
- Full Password Vault Web Access – This option installs the PVWA for desktop browsers.
- Mobile Password Vault Web Access – This option installs a PVWA interface that is specifically for mobile devices.
4. Click Next to proceed to the Web application details window, which enables you to specify the web site name, application name, and authentication type(s) for the web application.
5. Click next to specify the username and password of the Vault user carrying out this installation, then click Next to create the Password Vault Web Access environment and display the Setup Complete window.
POST Installation
- Installation log review
- “C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\”.
- Installation verify
- Log in to your PVWA with Vault Administrator user
- IIS Configuration Change
- Error Code 403 – Redirect http to https
- Automatic Hardening
- run hardening script
- Manual Hardening – General Security For PVWA to meet CyberArk Security Standard
- Service verification (Just one service for PVWA)
- CyberArk Scheduled Tasks is running
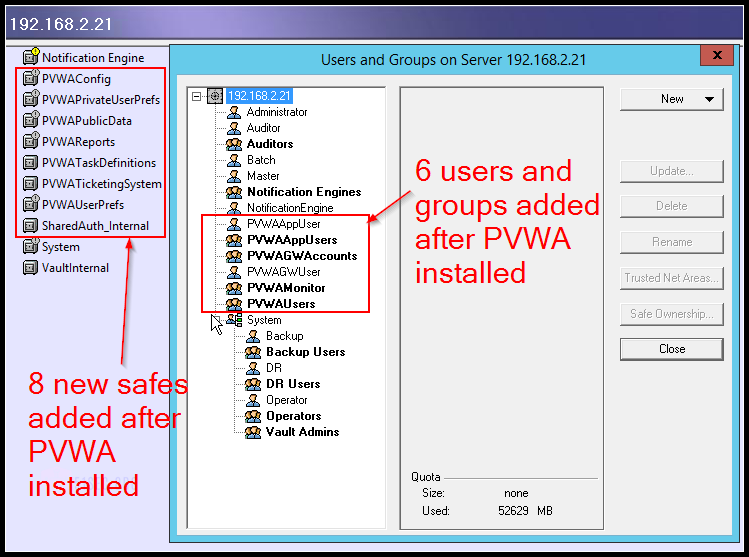
Vault Changes after PVWA installed
CreateCredFile Utility
The Vault interfaces access the Vault with a user credential file that contains the user’s Vault username and encrypted logon information. This user credential file can be created for password, Token, PKI, or Radius authentication with a utility that is run from a command line prompt. It can also create a credentials file for authentication through a Proxy server.
| ■ | Specific application – The credentials file can only be used by a specific CyberArk application or module. This can be specified for Password, Token, or PKI authentication but not for Proxy authentication. For more details about specific applications, refer to CreateCredFile Utility. |
| ■ | Specific path – The credentials file can only be used by an executable located in a certain path. |
| ■ | IP address or hostname – The credentials file can only be used on the machine where it is created. |
| ■ | Operating System user – The credentials file can only be used by an application started by a specified Operating System user. |
References