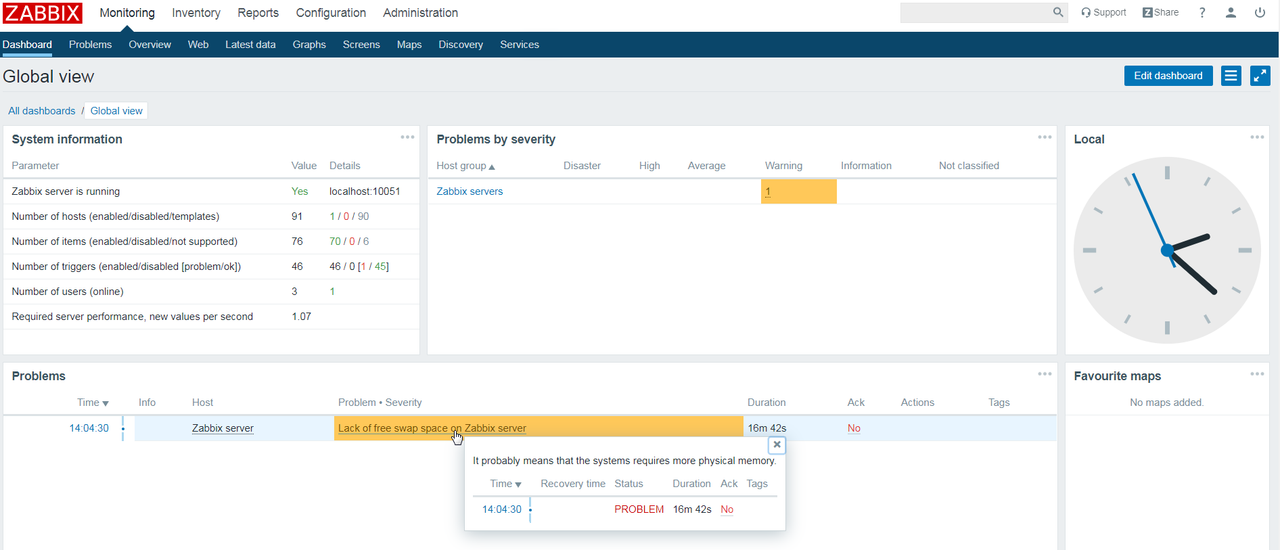
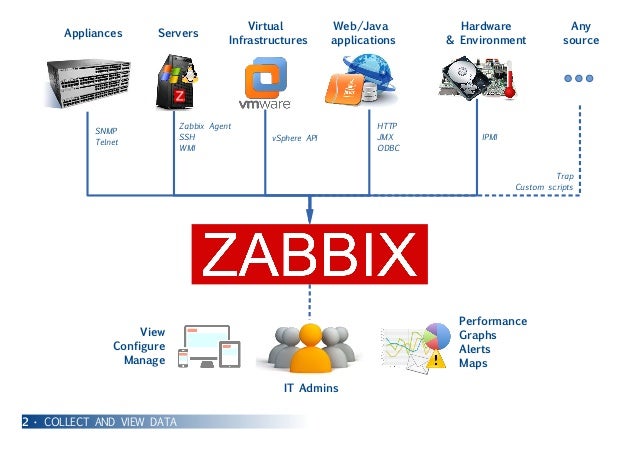
 Zabbix is a mature and effortless enterprise-class open source monitoring solution for network monitoring and application monitoring of millions of metrics. This post is going to install zabbix4.0 into a brand new Centos7.x system environment, including default installation of mariab5.5, php5.4, apache2.4 as well.
Zabbix is a mature and effortless enterprise-class open source monitoring solution for network monitoring and application monitoring of millions of metrics. This post is going to install zabbix4.0 into a brand new Centos7.x system environment, including default installation of mariab5.5, php5.4, apache2.4 as well. YouTube Video:
Notes: Before you can install Zabbix, you might want to exclude Zabbix from SELinux disable SELinux and Firewall.
Note: I have used Google Cloud Platform free tier vm (1vCPU, 614MB Memory and 10G Hard Drive) to complete this installation without problem. If you have bigger space and large memory, that would be better.
1. Install the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) source
yum update
yum -y install epel-release
rpm -qa | grep zabbix
rpm -ql zabbix-release
cat /etc/yum.repos.d/zabbix.repo
2. Install php-fpm and mariadb
3. Configure zabbix4.0 source
rpm -ivh https://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/4.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-release-4.0-1.el7.noarch.rpm
4. Install zabbix4.0 software
yum -y install zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-web-mysql zabbix-agent
5. Start and Enable mariadb
systemctl start mariadb
6. Configure mariadb for Zabbix to use
mysql -uroot -p
MariaDB [(none)]> create database zabbix character set utf8 collate utf8_bin;
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on zabbix.* to zabbix@localhost identified by ‘zabbixdbpassword’;
MariaDB [(none)]> quit
Import zabbix data:
zcat /usr/share/doc/zabbix–server–mysql*/create.sql.gz | mysql –uzabbix –pzabbixdbpassword zabbix
7. Modify the zabbix-server configuration file
vi /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf
DBHost=localhost
DBName=zabbix
DBUser=zabbix
DBPassword=zabbixdbpassword
If the account password here is inconsistent with the actual account password you set, when you start zabbix-server, you can’t see the port, but you can see the process!
8. Modify the php timezone configuration
|
date.timezone = “America/New_York”
|
9. Start related services
systemctl enable php-fpm
systemctl start php-fpm
systemctl enable httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable zabbix-server
systemctl start zabbix-server
systemctl enable zabbix-agent
systemctl start zabbix-agent
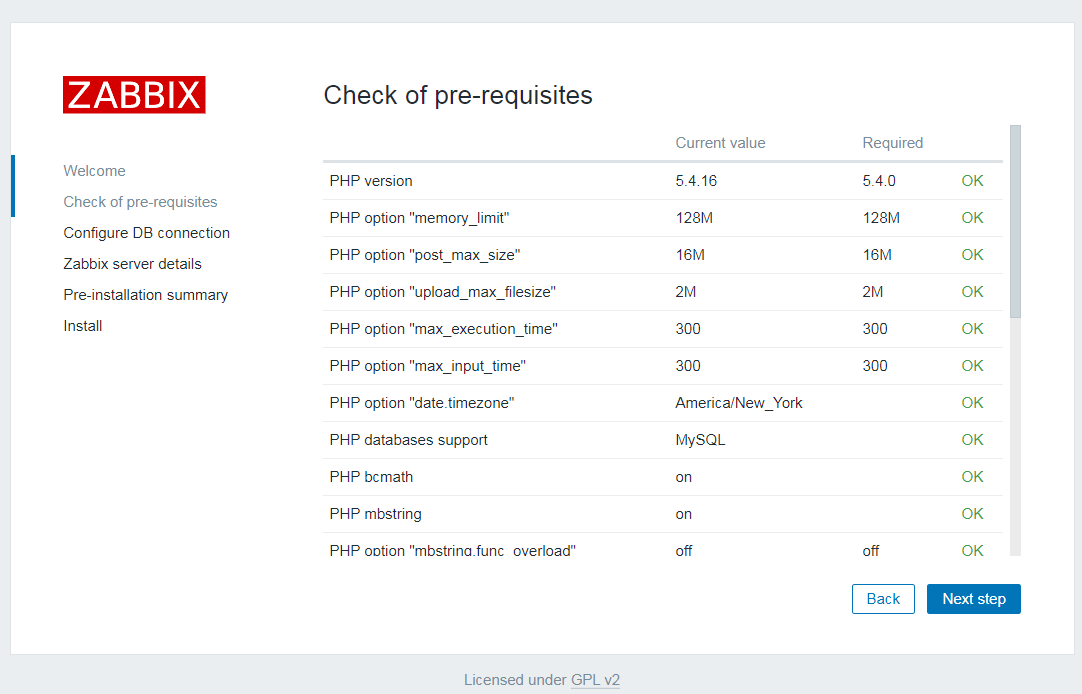
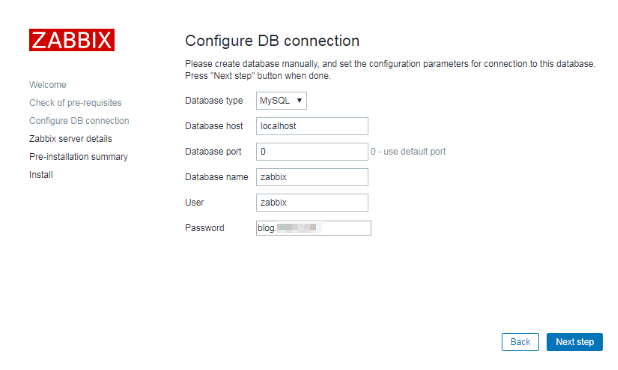
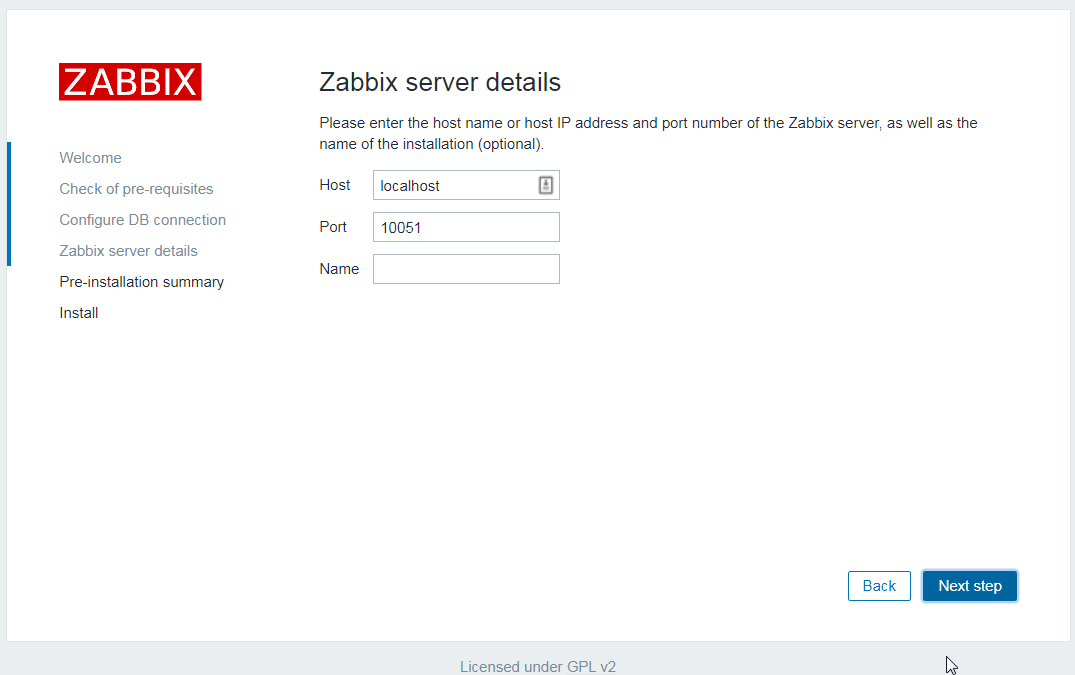
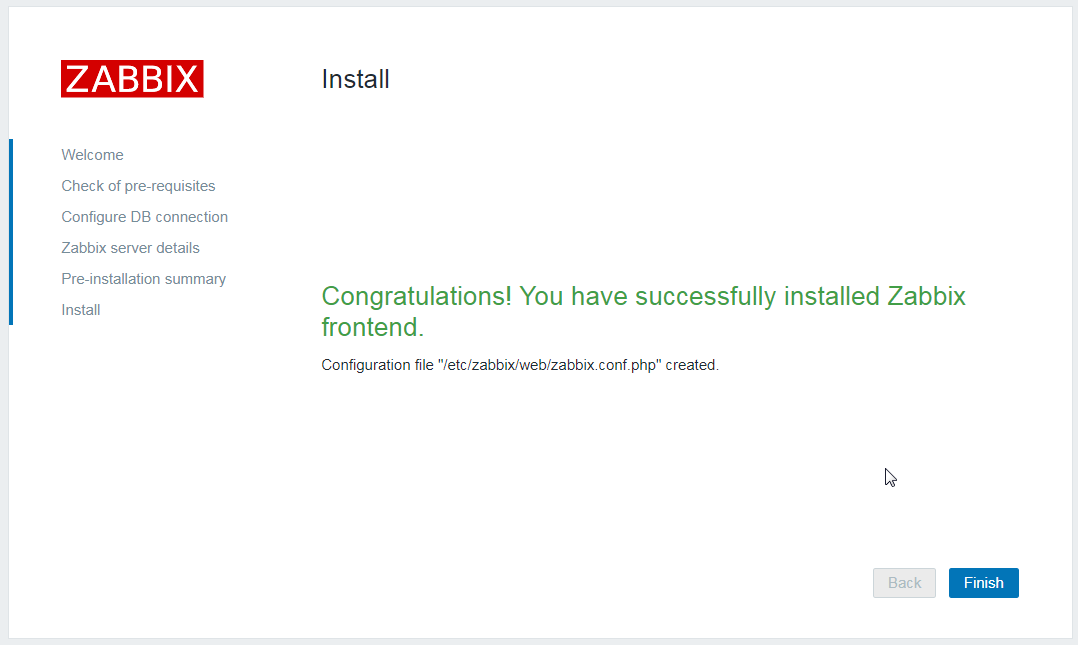
10. Enter the web installation
Another YouTube Video to install Zabbix Virtual Appliance:
Troubleshooting
Issue 1 : You might get one error to say “Zabbix server is running” but value is no. Basically, zabbix server is not started properly.
From the /var/log/zabbix/zabbix_server.log, you will find following information:
[root@linux1centos1 zabbix]# tail zabbix_server.log
5828:20191019:195018.548 server #20 started [trapper #1]
5830:20191019:195018.551 server #22 started [trapper #3]
5831:20191019:195018.554 server #23 started [trapper #4]
5838:20191019:195018.556 server #30 started [preprocessing manager #1]
5838:20191019:195018.556 cannot start preprocessing service: Cannot bind socket to “/var/run/zabbix/zabbix_server_preprocessing.sock”: [13] Permission denied.
5804:20191019:195018.558 One child process died (PID:5838,exitcode/signal:1). Exiting …
zabbix_server [5804]: Error waiting for process with PID 5838: [10] No child processes
5804:20191019:195018.632 syncing trend data…
5804:20191019:195018.632 syncing trend data done
5804:20191019:195018.632 Zabbix Server stopped. Zabbix 4.0.13 (revision 4e383bb6c5).
Usually it is relating to selinux status. By default it has been enabled and it will give Zabbix service a problem to start.
Disable SELinux
targeted to permissive with the following command:sudo setenforce 0
-
Open the
/etc/selinux/configfile and set theSELINUXmod todisabled:/etc/selinux/config# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted -
Save the file and reboot your CentOS system with:
sudo shutdown -r now -
Once the system boots up, verify the change with the
sestatuscommand:sestatusThe output should look like this:SELinux status: disabled
Stop/Disable CentOS Firewall
sudo firewall-cmd –state
sudo systemctl stop firewalld
sudo systemctl disable firewalld
sudo systemctl mask --now firewalld