Portainer is a lightweight management UI which allows you to easily manage your different Docker environments (Docker hosts or Swarm clusters). It is meant to be as simple to deploy as it is to use. It consists of a single container that can run on any Docker engine (can be deployed as Linux container or a Windows native container). Portainer allows you to manage your Docker containers, images, volumes, networks and more !
1. Installation in CentOS / Ubuntu
1.1 CentOS 7/Debian 9
Here is an easiest way to install docker into your CentOS / Debian system. It is just one command:
curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh
Start docker service and enable it when system started
sudo -isystemctl start docker.service systemctl enable docker.servicecreate a volume dedicated for Portainer's data storage:
docker volume create portainer_datause docker command to run Portainer container:
docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --name portainer --restart always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer1.2 Ubuntu
System updatesudo apt update sudo apt upgradeInstall docker into Ubuntu:
sudo apt install docker.io -yStart docker service and enable it when system started
sudo -isystemctl start docker systemctl enable dockerdocker versioncreate a volume dedicated for Portainer's data storage:
docker volume create portainer_datause docker command to run Portainer container:
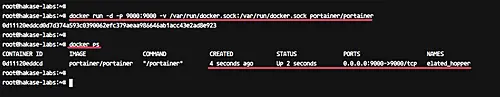
docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --name portainer --restart always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainerdocker ps2. Log into Portainer Web Gui
Use your browser to access URL http://<public ip of your linuxserver>:9000
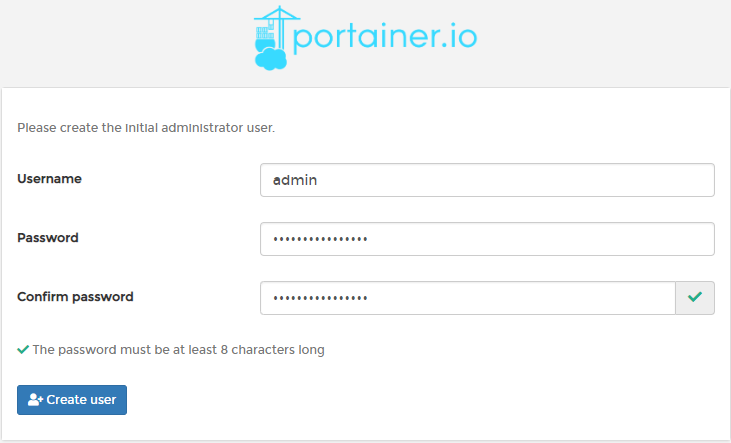
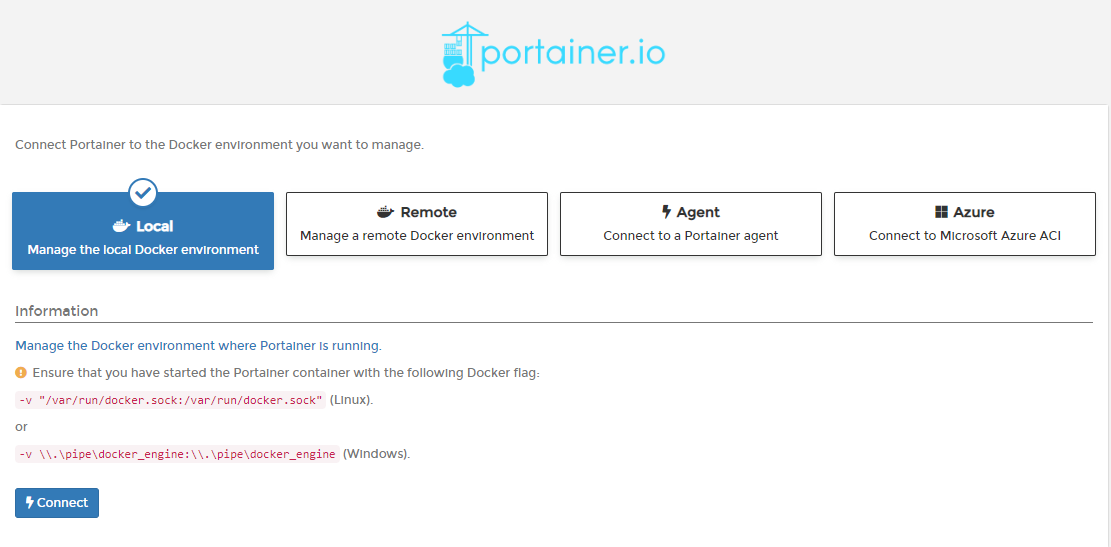
First time, it will ask you to set up admin user's password.Since portainer is deployed on local machine and we are managing it from local, we will choose local to connect.
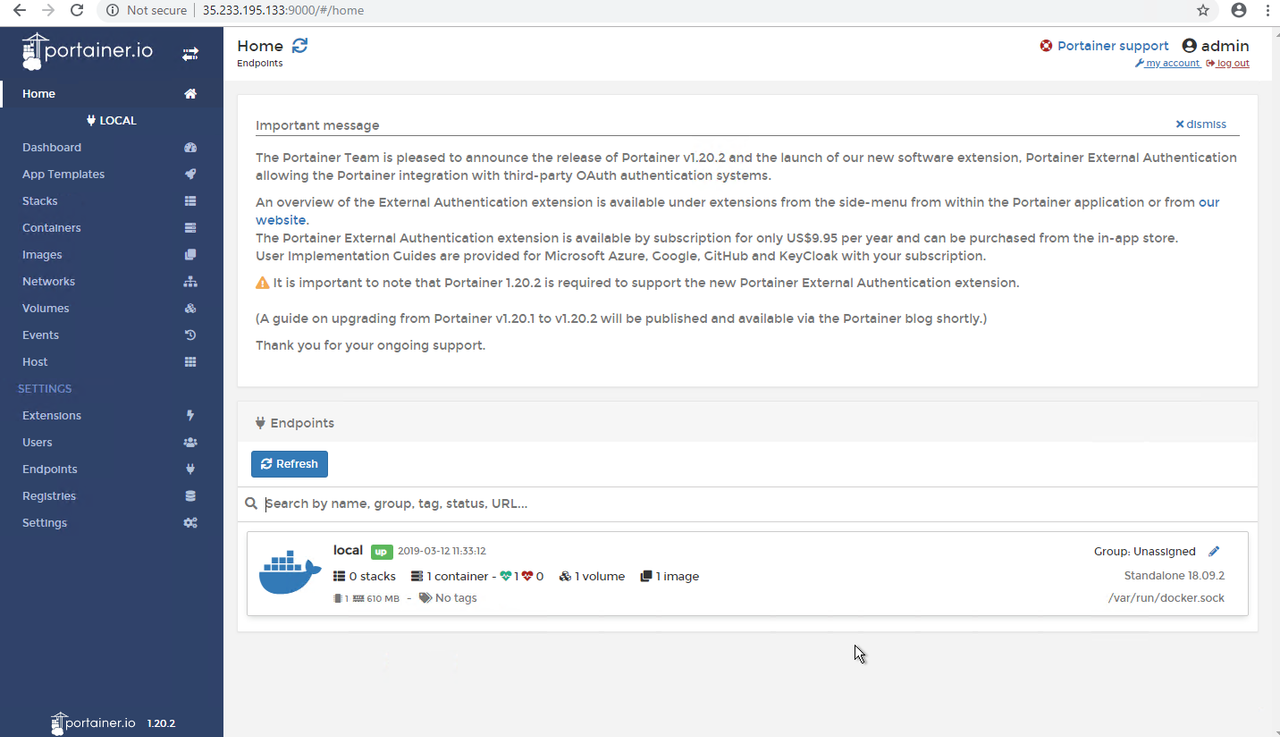
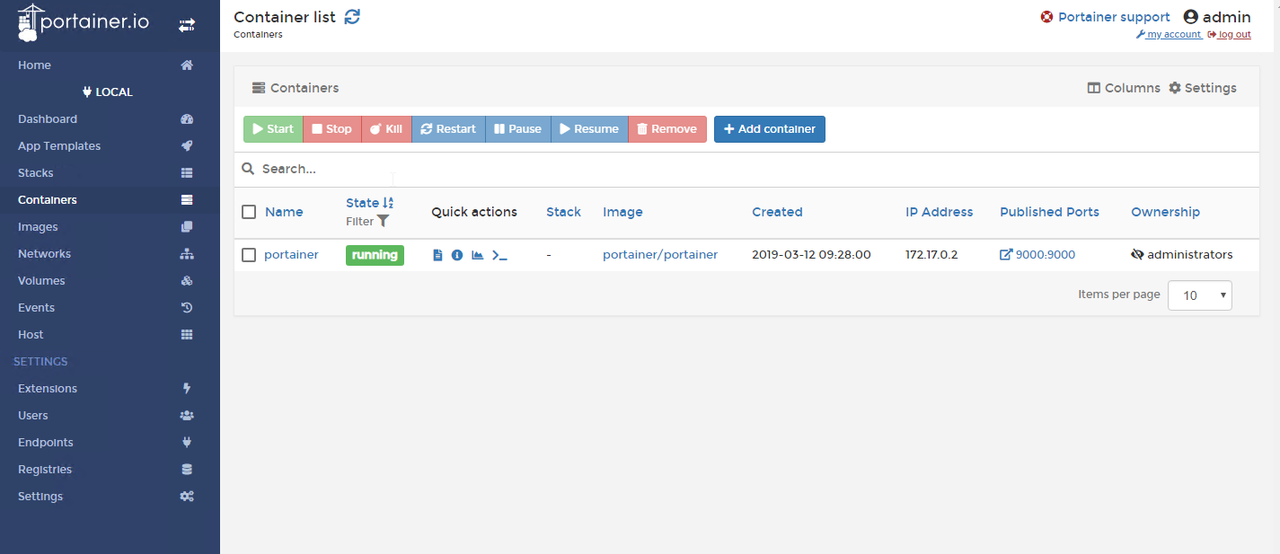
Now it is Portainer's home page.
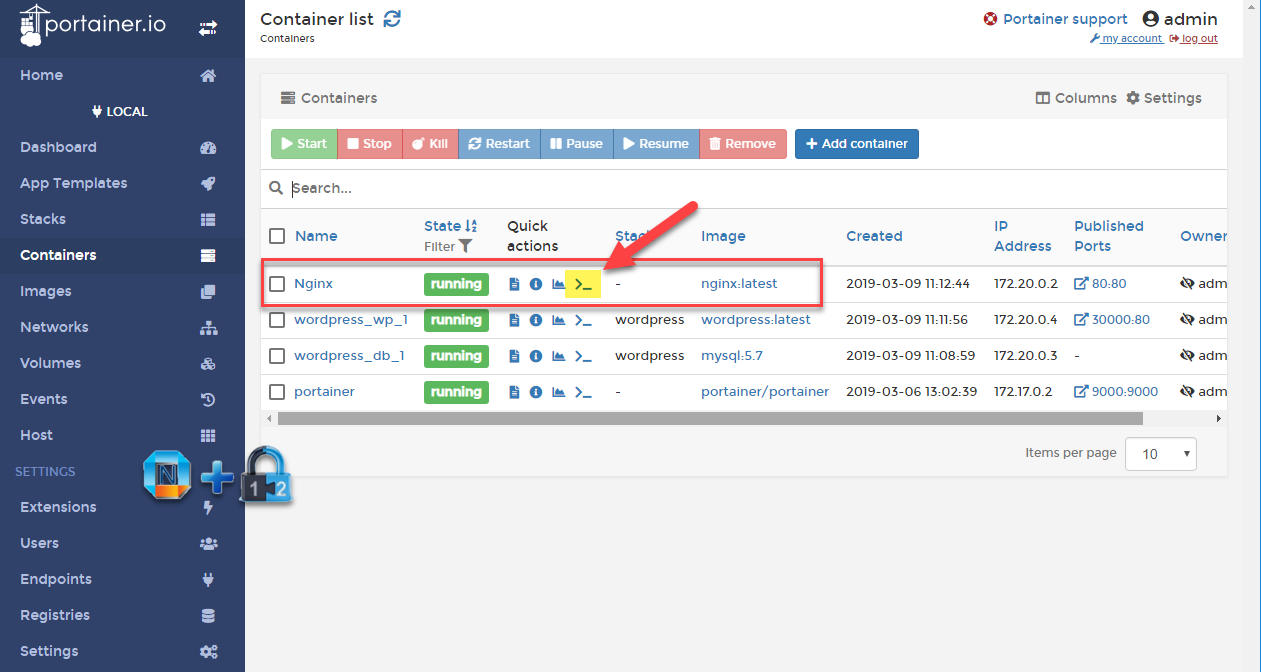
As you can see from the following screenshot, Portainer container has been deployed.
3. Deploy WordPress App Container
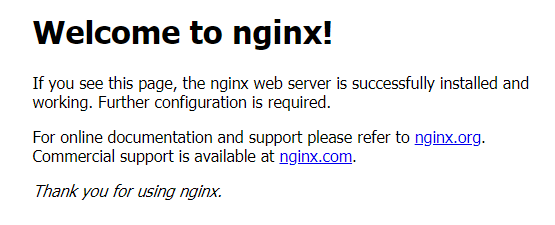
3.1 Deploy Nginx
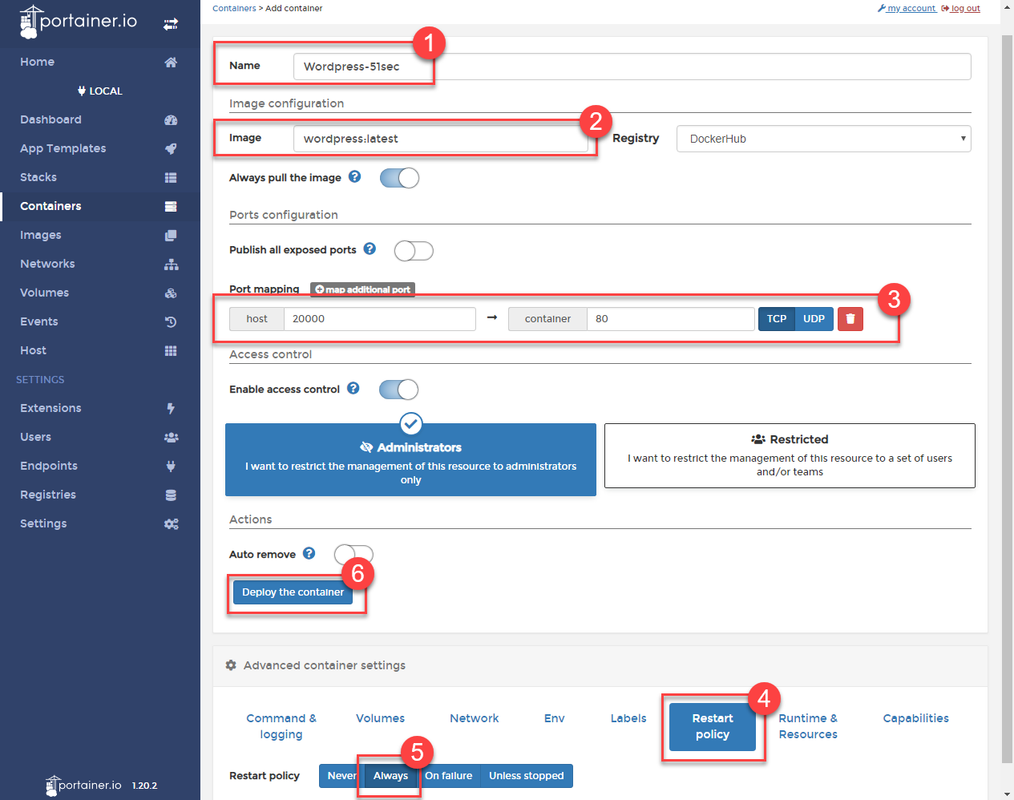
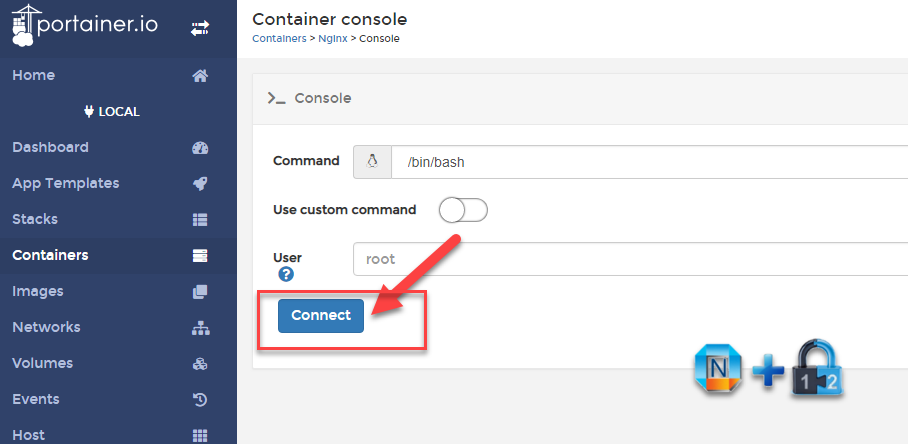
Click button "+Add container" and enter following information for Nginx container.
You can use your browser to access your virtual machine's public ip to confirm nginx is runing.
3.2 Deploy MySQL DB - MariaDB
There are two environment variables need to be added in.
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORDMYSQL_DATABASEAlso do not forget to change Restart policy to always to make sure your container survive system reboot.
3.3 Deploy WordPress
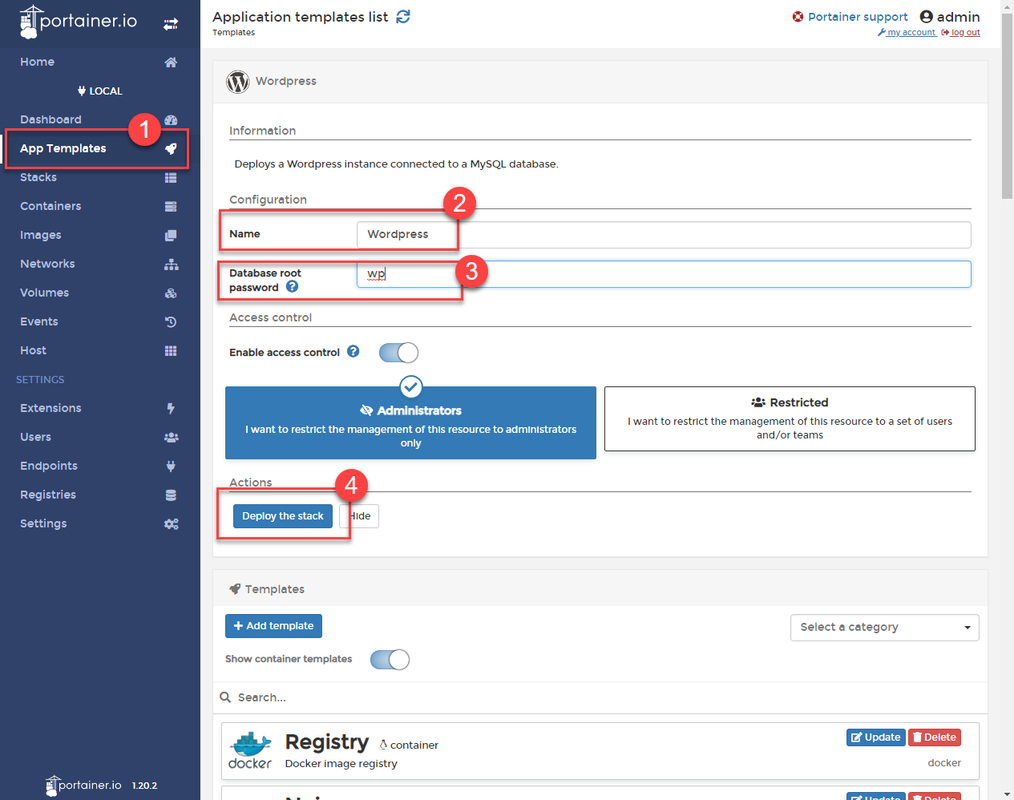
Or You can deploy WordPress Stack to add WordPress and MySql at the same time, which is the way I prefer.
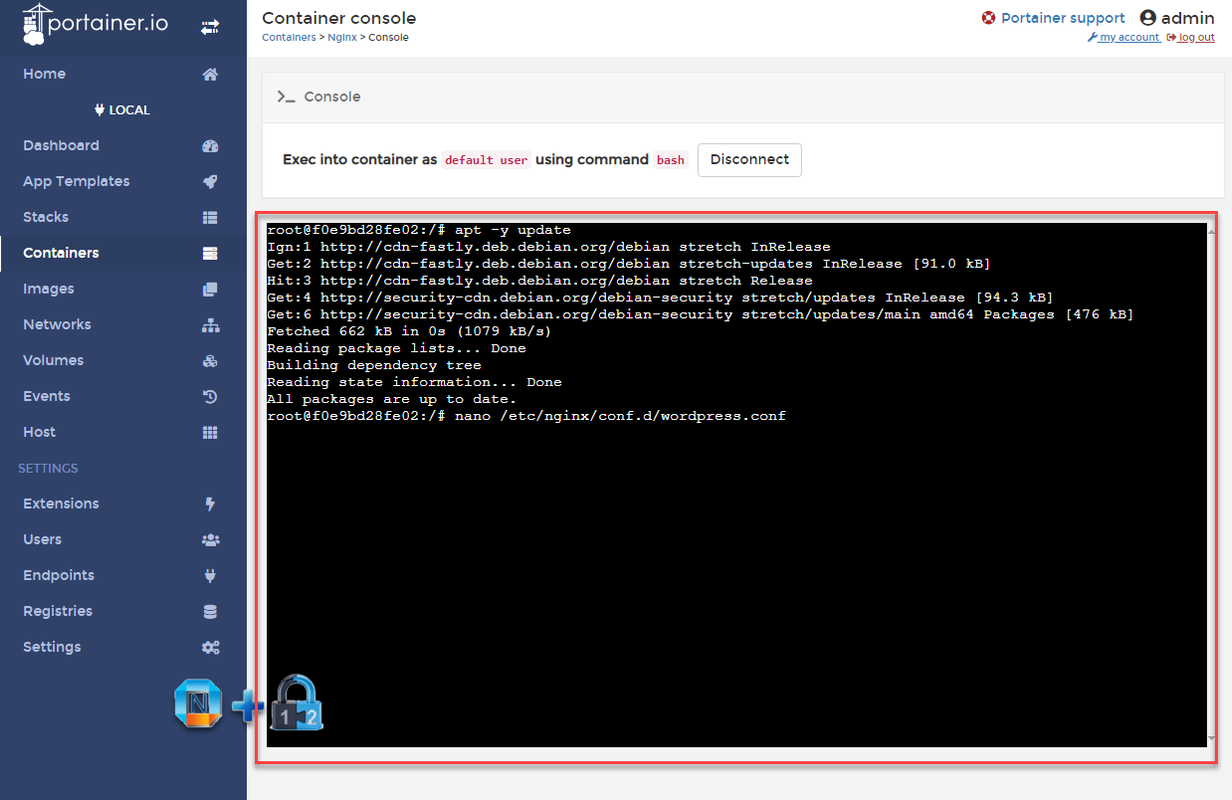
3.4 Configure Nginx Reverse Proxy
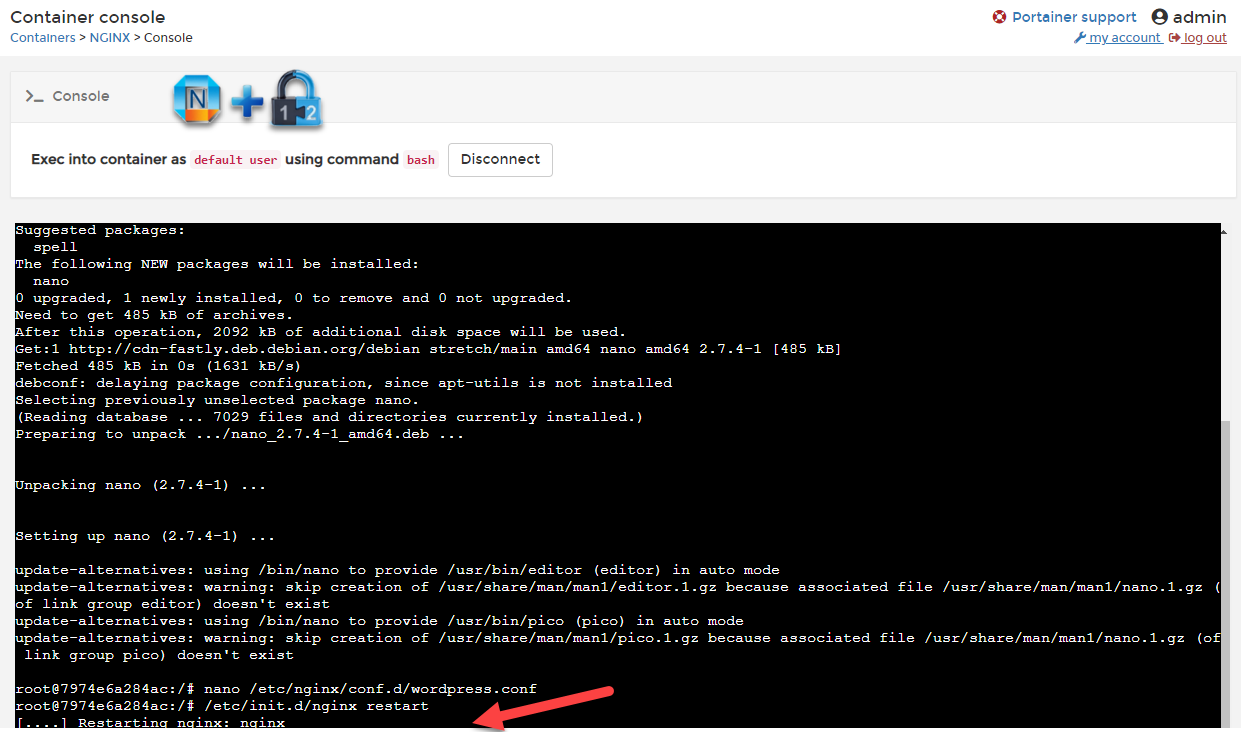
apt -y update apt -y install nanocreate a wordperss Nginx configuration file:nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/wordpress.confcopy following configuration into the file:(make sure to change port 80, server_name and proxy_pass to your own configuration)server { listen 80; server_name www.51sec.org 51sec.org; location / { proxy_pass http://3.45.23.194:20000; proxy_redirect off; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } }
Once saved the conf file, restart nginx service to apply the new configuration.
/etc/init.d/nginx restart
There is a bug for command /etc/init.d/nginx restart. The restarting nginx status will not change although restarting procedure has been completed.
3.5 Configure Nginx to do load balance
If you have multiple sites, you can configure Nginx to load balance between multiple servers.
There are two files you will need to change:root@f0e9bd28fe02:/# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf user nginx; worker_processes 1; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn; pid /var/run/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { upstream mysec { ip_hash; server 3.81.70.239:30000 weight=3; server 34.73.78.142:80 weight=2; } include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; } root@f0e9bd28fe02:/#
root@f0e9bd28fe02:/# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/wordpress.conf server { listen 80; server_name www.51sec.org; location / { proxy_pass http://mysec; proxy_redirect off; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; } } root@f0e9bd28fe02:/#Another simple Nginx Load Balance Configurationhttp { upstream project1 { server 127.0.0.1:8000 weight=3; server 127.0.0.1:8001 weitht=2; server 127.0.0.1:8002; } server { listen 80; server_name www.51sec.org; location / { proxy_pass http://project1; } } }Related YouTube Videos:
References: