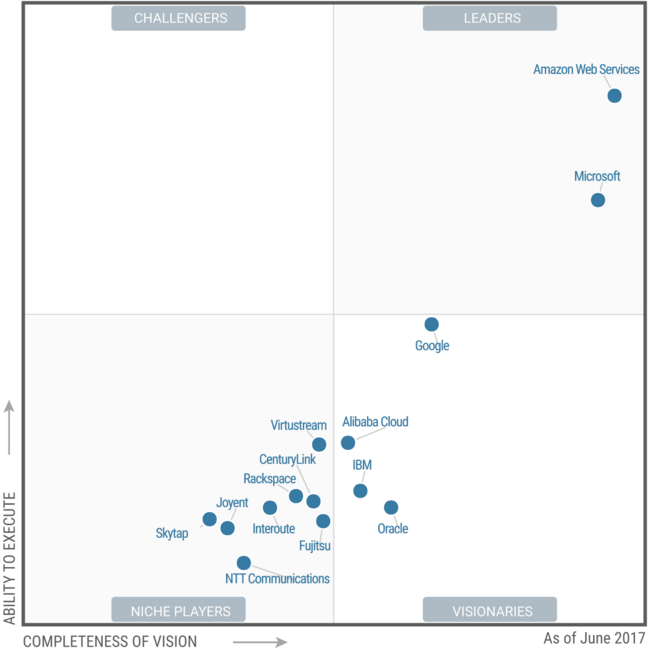
| Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure as a Service, Worldwide June 2017. |
According to Gartner, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has became as the undisputed leading cloud provider in the world. AWS is rated “the most mature, enterprise-ready provider, with the deepest capabilities for governing a large number of users and resources.” Gartner says it can satisfy the cool kids who want cloud-native and old hands who want to shift traditional workloads to the cloud, in part because independent software vendors have clambered aboard in large numbers.
AWS has a good documentation Quick Start deployment guide which present a good example to build a VPC environment with the following features:
- Up to four Availability Zones for high availability and disaster recovery. Availability Zones are geographically distributed within a region and spaced for best insulation and stability in the event of a natural disaster. AWS recommends maximizing your use of Availability Zones to isolate a data center outage.
- Separate subnets for unique routing requirements. AWS recommends using public subnets for external-facing resources and private subnets for internal resources. For each Availability Zone, this Quick Start provisions one public subnet and one private subnet by default.
- Additional layer of security. AWS recommends using network access control lists (ACLs) as firewalls to control inbound and outbound traffic at the subnet level. This Quick Start provides an option to create a network ACL protected subnet in each Availability Zone. These network ACLs provide individual controls that you can customize as a second layer of defense.
- Independent routing tables configured for every private subnet to control the flow of traffic within and outside the Amazon VPC. The public subnets share a single routing table, because they all use the same Internet gateway as the sole route to communicate with the Internet.
- Highly available NAT gateways, where supported, instead of NAT instances. NAT gateways offer major advantages in terms of deployment, availability, and maintenance.
- Spare capacity for additional subnets, to support your environment as it grows or changes over time.
1. Log into AWS Console
 |
| AWS Console |
 |
| AWS Services |
 |
| EC2 Console |
2. Building a stable and secure AWS foundation (VPC, AMI)
2.1. Create your VPC
Amazon VPC – The Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) service lets you provision a private, isolated section of the AWS Cloud where you can launch AWS services and other resources in a virtual network that you define. You have complete control over your virtual networking environment, including selection of an IP address range, creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and network gateways.
 |
| VPC Console |
 |
| VPC Wizard 1 |
 |
| VPC Wizard 2 |
 |
| VPC Wizard 3 |
Note: With VPC creating wizard, there are many components created for this vpn automatically.
2.2. Create your Internet Gateway
By default , Internet Gateway has been created when you created your own VPC by step 2.1 wizard .
2.3. Create your Subnets
There will be a subnet automatically created for you by step 2.1 wizard.
2.4. Create your route table
There will be two route tables automatically created for you by step 2.1 wizard.
2.5. Create your IAM (Identiy and Access Management)
Services-Security , Identity & Compliance
 |
| AWS IAM Console |
 |
| IAM Set Permissions |
 |
| Add Group with two Permissions – EC2 Full and read only |
 |
| AWS IAM User Create review |
 |
| Deny access for S3 |
Note: the permissions you will get is the maximum one configured in the group.
References:
| Scenario | Usage |
|---|---|
|
Use the VPC wizard to create a VPC for running a single-tier, public-facing web application such as a blog or simple web site.
|
|
|
Use the VPC wizard to create a VPC for running a public-facing web application, while still maintaining non-publicly accessible back-end servers in a second subnet.
|
|
|
Use the VPC wizard to create a VPC for extending your data center into the cloud, and also directly access the Internet from your VPC.
|
|
|
Use the VPC wizard to create a VPC for extending your data center into the cloud, and leverage Amazon’s infrastructure without exposing your network to the Internet.
|
|
|
Use the AWS CLI to create a VPC and and a public and private subnet.
|
|
|
Use the AWS CLI to create a VPC with an associated IPv6 CIDR block, and a public and private subnet each with an associated IPv6 CIDR block.
|