Different firewall (security gateway) vendor has different solution to handle the passing traffic. This post compiles some useful Internet posts that interpret major vendors’ solutions including:
1. Checkpoint
2. Palo Alto
3. Fortigate
4. Cisco
5. Juniper
6. F5
1. Checkpoint Firewall Packets Flow:
Note: Checkpoint can define destination NAT happens at client side (default) or server side. Source NAT always at outbound, and ACL is checked before NAT. More details are on SK85460
Also you could check the packet inspection order/chain through gateway command line.(It will be different based on your enabled features):
1.1 FW-CP1> fw ctl chain
in chain (18):
0: -7f800000 (f28854f0) (ffffffff) IP Options Strip (in) (ipopt_strip)
1: -7d000000 (f1796f10) (00000003) vpn multik forward in
2: – 2000000 (f177cb70) (00000003) vpn decrypt (vpn)
3: – 1fffff8 (f1787c00) (00000001) l2tp inbound (l2tp)
4: – 1fffff6 (f2886ca0) (00000001) Stateless verifications (in) (asm)
5: – 1fffff5 (f28bce30) (00000001) fw multik misc proto forwarding
6: – 1fffff2 (f17a4df0) (00000003) vpn tagging inbound (tagging)
7: – 1fffff0 (f177a150) (00000003) vpn decrypt verify (vpn_ver)
8: – 1000000 (f29049c0) (00000003) SecureXL conn sync (secxl_sync)
9: 0 (f282f810) (00000001) fw VM inbound (fw)
10: 1 (f28a6b30) (00000002) wire VM inbound (wire_vm)
11: 2000000 (f177b5e0) (00000003) vpn policy inbound (vpn_pol)
12: 10000000 (f2902cb0) (00000003) SecureXL inbound (secxl)
13: 7f600000 (f287ab70) (00000001) fw SCV inbound (scv)
14: 7f730000 (f2a13500) (00000001) passive streaming (in) (pass_str)
15: 7f750000 (f2c0bef0) (00000001) TCP streaming (in) (cpas)
16: 7f800000 (f2885890) (ffffffff) IP Options Restore (in) (ipopt_res)
17: 7fb00000 (f2fac050) (00000001) HA Forwarding (ha_for)
out chain (15):
0: -7f800000 (f28854f0) (ffffffff) IP Options Strip (out) (ipopt_strip)
1: -78000000 (f1796ef0) (00000003) vpn multik forward out
2: – 1ffffff (f1779a10) (00000003) vpn nat outbound (vpn_nat)
3: – 1fffff0 (f2c0bd70) (00000001) TCP streaming (out) (cpas)
4: – 1ffff50 (f2a13500) (00000001) passive streaming (out) (pass_str)
5: – 1ff0000 (f17a4df0) (00000003) vpn tagging outbound (tagging)
6: – 1f00000 (f2886ca0) (00000001) Stateless verifications (out) (asm)
7: 0 (f282f810) (00000001) fw VM outbound (fw)
8: 1 (f28a6b30) (00000002) wire VM outbound (wire_vm)
9: 2000000 (f1779c30) (00000003) vpn policy outbound (vpn_pol)
10: 10000000 (f2902cb0) (00000003) SecureXL outbound (secxl)
11: 1ffffff0 (f17887b0) (00000001) l2tp outbound (l2tp)
12: 20000000 (f177d5b0) (00000003) vpn encrypt (vpn)
13: 7f700000 (f2c0e340) (00000001) TCP streaming post VM (cpas)
14: 7f800000 (f2885890) (ffffffff) IP Options Restore (out) (ipopt_res)
1.2 Checkpoint Example for Client Side NAT flow:
-
- The packet that was sent to Server’s NATed IP 172.16.0.100, arrives on the “Source/Client” side at the inbound interface eth0 of the Security Gateway (Pre-Inbound chains).
- The packet passes the Security Policy rules (inside Virtual Machine).
- If accepted, the connection is recorded in the Connections Table (Table ID 8158).
- The packet is matched against NAT rules for the Destination. The packet is translated if a match is found – in this case, from IP 172.16.0.100 to IP 10.0.0.100.
- The packet passes additional inspection (Post-Inbound chains).
- The packet arrives at the TCP/IP stack of the underlying operating system, and is routed to the outbound interface eth1.
- The packet goes through the outbound interface eth1 (Pre-Outbound chains).
- The packet passes the Security Policy rules (inside Virtual Machine).
- The packet is matched against NAT rules for the Source (if such rules exist). The packet is translated if a match is found – in this case, no translation occurs.
- The packet passes additional inspection (Post-Outbound chains).
- The packet leaves the Security Gateway machine.

1.3 Checkpoint Policy Installation Flow from FW Knowledge Blog:
2. Fortigate FortiOS:
2.1 Packet flow Process:
2.2 Example for Client/server connection:
3. Palo Alto Traffic Flow:
 |
| Flow Logic of the Next-Generation Firewall |
4. Cisco IOS/ASA Traffic Flow:

There are more details regarding NAT order, ACL order etc from my previous post: Cisco IOS/ASA Packet Passing Order of Operation
5. JunOS Traffic Flow:
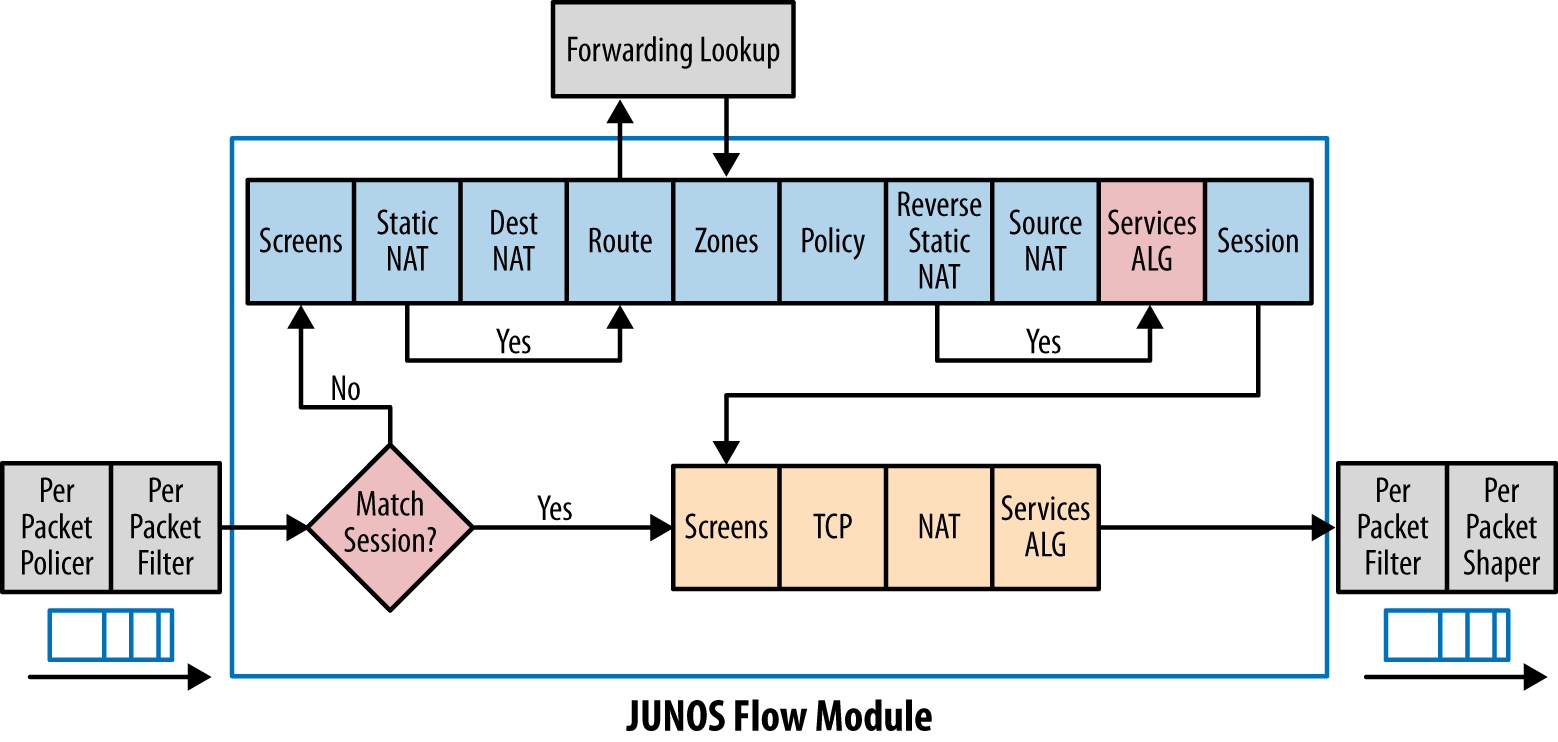 |
| JunOS Flow Module |
Next diagram with more details:
6. F5
 |
| TMOS Order of Operations – TCP Traffic Path Diagram |
 |
| F5 LTM Traffic Flow |
Following F5 architecture diagram is from Sinso’s Post:
Reference:
- How does the Security Gateway handle Established TCP Connections?
- JunOS Packets Flow
- Check Point Policy Installation Process
- CNSE -Palo Alto – Firewall configuration essentials
- Packet Flow Through Checkpoint
- FortiOS™ Handbook – Troubleshooting v5.2.2
- TCP Traffic Path Diagram










Hello,
Very interessting blog. Thanks.
For F5 products I suggest to use the following diagramm https://devcentral.f5.com/questions/tcp-traffic-path-diagram instead of physical architecture.
Best regards,
Arnaud
Thanks Amaud. I will put that in.
amazing post